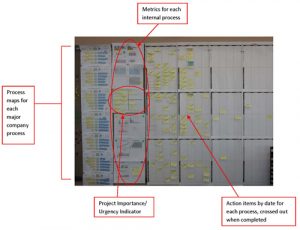
What is a Lean ISO QMS?
Building a Lean ISO QMS (Quality Management System) is about focus – less is more! Increasing focus means finding the vital few (i.e. critical) metrics that will focus all workers on the most important aspects of your business — your customer satisfaction.
What does a Lean ISO QMS look like?
Most, if not all, customers want the same thing: On Time Delivery (OTD), a good price, and good quality. This means they want their order when the Purchase Order (PO) specifies, not a promise date later than the PO and not when you actually ship after your promise date. They want OTD as per the PO. If your OTD is not 100% then your ISO QMS is not working.
Of course, they also want a good price, which means no overnight delivery to make OTD, no quality defects sorted out before delivery (they do not want to pay for your poor quality), no rework, no excessive inventory, or other manufacturing wastes. A Lean ISO Quality Management Systems is focused on constantly eliminating waste to drive down costs, increase quality and hit OTD 100% of the time.
Building both a Lean and ISO 9001 system requires increasing the process maturity of each Critical To Quality (CTQ) process in the ISO QMS and reducing waste.
How is this done?
- Improve (change) your structure
- Visualize waste through clear data, metrics, and expectations
- Increase worker capability
- Iterate waste out of the system
Opportunities for increasing process capability include: looking at maintenance effectiveness, management, labor relations, employee competence, quality–preferably the Cost Of Quality (COQ), and inventory that results from delays, setup time, batch size and supply chain effectiveness.
Lean ISO QMS Value
What is a Lean Quality Management System? Focusing on OTD means focusing all work centers on throughput, one of the primary needs of any company. Throughput is reduced by losses due to planned maintenance, unplanned maintenance, defects, rework, delays, and process effectiveness. A higher degree of precision from individually balanced processes can deliver greater control over these losses and increase overall throughput.
Benefits of a Lean ISO QMS
- Builds teamwork
- Provides actionable data
- Focuses employees on CTQ processes
- Delivers value from your ISO system
- Enables higher levels of quality
How to Create a Lean ISO QMS
Building a Lean ISO Quality System requires building teamwork with managers and supervisors acting as team leaders, identifying value added and non-value added activities, and developing clear process boundaries, effectiveness criteria, and communication that creates value chains within the organization. Let’s look at the three main steps to creating a Lean ISO QMS.
Scope the Lean ISO Project
First, finalize the scope of the project management. The initial scope should focus on transitioning the current ISO QMS to a Lean ISO QMS. Identify your current levels of teamwork, data, metrics, CTQ processes, employee competence, and overall effectiveness are. This is your current state.
Form the ISO Steering Committee
Second, assemble an ISO steering committee to transition to a Lean ISO 9001 Quality Management System. The committee should be comprised of key management personnel that are the process owners of the CTQ processes.
Proposed steering committee:
- Management
- Quality
- Product Realization
- Sales/Order Acceptance
- Design & Development
- Purchasing
- Shipping, Receiving, Warehouse
- Human Resources
- Preventive Maintenance
- Laboratory
- Information Technology
- Measurement & Instrumentation
Finalize the Lean ISO Project Plan
Third, finalize a project plan with clear milestones, deliverables, and action steps to ensure the project completes on time.
Expected deliverables for a working ISO QMS that adds value to the management team include:
- Reduced non-value added documentation that does not work demonstrating a Lean ISO QMS derived from value added activities, CTQ work performed, and CTQ data collected.
- Employee involvement demonstrating working value chains derived from teamwork, improved satisfaction, and people taking the initiative to drive results.
- Revised quality objectives demonstrating measures of improvement derived from management team leaders identifying value added and non-value added activities, developing clear process boundaries, effectiveness criteria, and communication.
- Data that tracks the performance of key processes, which will provide management with a formalized method to continually improve each process and the overall operation.
All of these Lean activities are designed to provide actionable data that focuses employees on the CTQ processes in order to deliver value from your ISO system. A solid QMS foundation enables an easier transition to higher levels of quality, effectiveness, and value.
Lean ISO QMS Project Plan
Improvement requires iterations. A lean ISO 9000 QMS is achieved through elimination and iteration. The core principles involve:
- Structure creates results
- You manage what you measure
- Visible waste gets eliminated
- Competent capable workers deliver results
The project plan is designed to build structure, focus on results, identify non-value added activities and motivate workers to deliver results. Each core process, process criteria, and method is involved to increase the focus and effectiveness of the QMS.
Six Phases of Lean QMS Project Plan
At bizmanual, when we implement a Lean ISO QMS project, it is done in six phases.
- Clause 4 Define Interested Parties, CTQ processes and system scope
- Clause 9.2, 8.7 & 10 Define continuous improvement activities
- Clause 5 -7 Direct continuous improvement activities and record training
- Clause 8 Define all Product Realization activities
(Planning, Sales, D&D, Purchasing, Manufacturing and Testing Eq) - Clause 9 Develop monitoring and measuring activities
- Preparation for Certification
This is typically done in six month consulting engagement. Work is conducted both onsite and in our office in St. Louis, MO. It is expected that each phase includes: site visits along with follow-up communication.
Each phase consist of:
- steering committee meetings to review progress,
- training, as needed,
- individual sessions with process owners,
- a small internal audit,
- management review, and
- action items for the next month.
Estimated cost of Lean ISO QMS
Cost varies by the size of the project. To determine the cost of the project, perform a Gap Analysis, which quantifies the level of effort. The goal is to deliver improvements in throughput via process capability, risk management, labor relations, and delays. A 1% change in throughput performance could produce a 20 times ROI for a project.
Could you use a Lean ISO Quality Management System?
One that delivers your products on time, at a fair cost and with good quality? If you have a lot of inventory (turns < 10), scrap, delays, large batch sizes (>1), delays (2 week lead times), poor OTD (< 100%), long setup times (> 5 minutes), or poor process capability (Cpk <1) then you need a Lean ISO QMS today. Contact us to see how increasing your focus would work at your organization. Lean is not expensive, it’s not being lean that is costing you money today.