What is the Difference Between ITIL and COBIT?
ITIL and COBIT are both popular IT frameworks in the tech world. They have distinct differences though. ITIL focuses on service management and improving customer satisfaction, while COBIT is all about governance and control. What is the Difference Between ITIL and COBIT?
ITIL and COBIT
ITIL is all about practices to manage IT services. It highlights understanding customer needs and continually improving service delivery. It also encourages streamlining processes to provide value to customers.
COBIT focuses on governance and control. It helps align IT activities with business objectives, manage risks, and meet regulatory requirements.
These two frameworks don’t have to be exclusive. Many organizations use both ITIL and COBIT. By combining these two, companies can achieve a balance between service quality and strategic alignment.
For instance, a multinational bank combined ITIL and COBIT for their IT operations. They adopted ITIL practices for improved customer satisfaction and efficient incident resolution. Then, they incorporated COBIT into their governance framework. This enabled them to strengthen control over their IT activities, while meeting regulatory requirements.
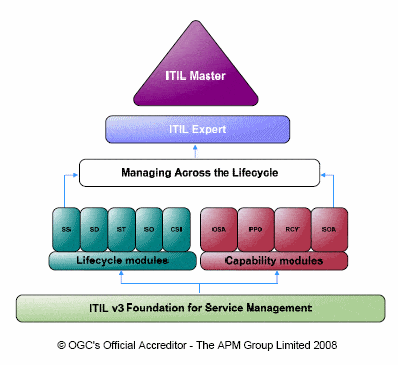
Overview of ITIL
ITIL is all about improving efficiency, reducing costs, and increasing customer satisfaction through high-quality IT services. It can be summarized in three pillars: Service Strategy, Service Design, and Service Transition. Unlock the power of these pillars by implementing them in your organization for a competitive edge!
Service Strategy focuses on aligning IT service objectives with business goals. Key components include defining the organization’s vision, conducting market research, and developing financial management processes.
Service Design encompasses designing new or modified services to meet business requirements. Key components include creating service portfolios, designing service architectures, and defining service level agreements (SLAs).
Service Transition covers the process of implementing new or modified services into production. Key components include managing change requests, testing services, and executing service releases.
Don’t miss out on the opportunity to leverage the power of ITIL! Implement these proven methodologies for improved operational efficiency, better decision-making, and enhanced customer experience. Get ready to unleash the full potential of ITIL and soar towards success!
Overview of COBIT
COBIT, or Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, is a renowned framework to help organizations govern and manage their IT processes. It provides guidance to connect IT goals to business objectives, ensuring maximum value delivery whilst reducing risk.
Let’s explore the fundamental parts of COBIT:
- Domain: Governance and Management Objectives. Description: Establishes strategic alignment, resource management, risk optimization, and performance measurement of IT governance.
- Domain: Processes. Description: Gives a comprehensive structure to organize IT activities into manageable processes according to business requirements.
- Domain: Process Activities. Description: Lists operational activities related to each process to obtain wanted results.
- Domain: Control Objectives. Description: Defines clear targets to ensure control over IT processes to achieve desired outcomes cost-effectively.
Firms find COBIT invaluable as it efficiently deals with various business issues. Through COBIT, companies can improve their decision-making processes, reduce risks adequately, and develop a reliable governance framework.
Don’t miss out on the advantages of COBIT! Embrace this powerful framework to revolutionize your firm’s IT governance and management practices. Lead the pack and unlock new chances for progress. Take action now!
ITIL and COBIT may seem like two acronyms fighting each other, however, one thing is certain – they both take IT governance seriously, as a little chaos with technology can cause huge problems.
Differences between ITIL and COBIT
ITIL and COBIT both have the same goal – to improve IT service management and governance. But there are key distinctions between them that make each framework unique.
To understand the differences, let’s compare their features in a table:
| Features | ITIL | COBIT |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Service-oriented | Control-oriented |
| Scope | Focused on service lifecycle management | Encompasses overall IT governance |
| Processes | 26 processes divided into five lifecycle stages | 37 processes grouped under four domains |
| Level of Detail | Provides more detailed guidelines and best practices for managing specific service areas | Offers a broader, high-level view of IT governance |
| Framework Structure | Based on a series of books with each book focusing on different aspects of the service lifecycle | Organized around four main domains: Plan and Organize, Acquire and Implement, Deliver and Support, Monitor and Evaluate |
These frameworks can be used independently, but they’re even better when used together. Organizations can combine the strengths of both ITIL and COBIT to get the most out of their IT services.
Pro Tip: Before implementing either framework, make sure to customize it according to your organization’s needs. This will help you get the most out of these frameworks while achieving your business objectives.
ITIL and COBIT may seem similar, but they’re like apples and oranges – each has their own special way of making your IT department question their life choices.
Similarities between ITIL and COBIT
ITIL and COBIT have similarities that are worth exploring. Both of these frameworks aim to improve IT service management practices. We’ll look at their key points to understand their common ground.
ITIL: Focuses on delivering value through IT services, establishes guidelines for service design, transition, and operation, and promotes continual service improvement.
COBIT: Aims to align IT governance with business goals, provides a comprehensive framework for managing and governing information technology, and emphasizes the need for effective controls and risk management in IT processes.
It’s clear that though these frameworks address different aspects, they still complement each other in several ways. Combining elements from ITIL and COBIT can result in a more holistic approach to governance, risk management, and compliance.
To make the most of this synergy:
- Integrate the frameworks.
- Set clear objectives.
- Foster collaboration.
- Review performance regularly.
- Embrace a culture of continuous learning.
By combining the strengths of both frameworks and following these suggestions, organizations can optimize operations, enhance service delivery, effectively mitigate risks, and align better with business goals. ITIL has the potential to revolutionize IT departments – just ask yours!
Advantages and Disadvantages of ITIL
ITIL–also known as the Information Technology Infrastructure Library–is a framework that provides guidelines for IT service management. It has some pros and cons that organizations must think about before implementing it. Let’s look at them in a table:
| Advantages of ITIL | Disadvantages of ITIL |
|---|---|
| 1. Improves customer satisfaction with quality services. | 1. Needs extensive training and resources to set up. |
| 2. Enhances communication and collaboration between IT and other teams. | 2. Can lead to complexity if not done right. |
| 3. Streamlines processes and keeps service delivery consistent. | 3. Can be time-consuming to tailor the framework to organizational needs. |
| 4. Helps in identifying and managing risks. | 4. Initial costs can be high for small organizations. |
| 5. Provides metrics for evaluating IT performance. | 5. Rigid structure may not fit every organization’s needs. |
Here’s something not many people know: ITIL works for small businesses, too–it just needs to be tailored to their specific needs.
Let me share a story: a software company implemented ITIL practices, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and an increase in repeat business.
In conclusion, while ITIL offers several benefits, there are challenges associated with its implementation that need to be taken into consideration.
Advantages and Disadvantages of COBIT
COBIT, a.k.a. Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, is a framework used by organizations to manage their IT processes. It has advantages and disadvantages to consider.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 1. Comprehensive framework for IT governance. | 1. Time-consuming and complex implementation. |
| 2. Aligns IT goals with business objectives. | 2. Significant financial investment for training and certification. |
| 3. Common language for IT pros and stakeholders. | 3. May cause rigid processes that inhibit agility. |
| 4. Addresses risks like data breaches or system failures. | 4. Not suitable for all organizations, especially smaller ones. |
Furthermore, COBIT helps set clear responsibilities and accountability for IT governance.
To understand COBIT, note that it promotes continuous improvement through assessments and reviews.
Conclusion: ITIL and COBIT are like two IT pros at a party. One focuses on best practices; the other ensures governance. Together, they make IT management a success!
Difference Between ITIL and COBIT
ITIL and COBIT have different focuses. ITIL mainly deals with IT service management, while COBIT’s scope is broader, covering governance and control. Both promote best practices, but vary in what they emphasize.
ITIL provides a system for IT service management. It outlines processes such as incident, change, and problem management. Following ITIL practices can enhance effectiveness and quality of service delivery. However, it doesn’t explore the controls needed for governance.
COBIT, on the other hand, focuses on giving comprehensive control and governance over enterprise-level information technology. It provides a framework to manage risks, meet regulations, and align IT goals with business objectives. It ensures transparency, accountability, and good stewardship of IT resources.
Which one is better? It depends on an organization’s needs. ITIL may be more beneficial for those optimizing their service management processes. For those needing a holistic approach to governance and control, COBIT may be more suitable.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is ITIL?
ITIL, which stands for Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a framework that provides best practices for managing IT services. It focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of the business and improving operational efficiency.
2. What is COBIT?
COBIT, which stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, is a framework that helps organizations govern and manage their information and technology processes. It provides a set of tools and guidelines for effective IT governance.
3. What is the main difference between ITIL and COBIT?
The main difference between ITIL and COBIT is their focus. ITIL primarily focuses on IT service management and aligning IT with business needs. COBIT, on the other hand, focuses on IT governance and provides a broader set of controls for managing IT processes and risks.
4. Which framework should I choose, ITIL or COBIT?
The choice between ITIL and COBIT depends on your organization’s specific needs and goals. If you want to improve IT service management and align IT with business needs, ITIL may be the right choice. If you are more concerned about IT governance and risk management, COBIT can be a better fit.
5. Can ITIL and COBIT be used together?
Yes, ITIL and COBIT can be used together. In fact, many organizations use both frameworks to benefit from their complementary strengths. ITIL provides guidance on IT service management processes, while COBIT provides a broader governance framework to ensure effective control and management of IT processes.
6. Are ITIL and COBIT certifications available?
Yes, certifications are available for both ITIL and COBIT. These certifications validate individuals’ knowledge and understanding of the respective frameworks. ITIL certifications are offered by AXELOS, while COBIT certifications are offered by ISACA.















Leave a Reply