What Cyber Framework Rules are used for IT?

Cybersecurity is an ever-evolving field, and organizations need to implement robust frameworks to protect their information assets. Several frameworks such as ITIL, COBIT, NIST, SOC2, ITSM, and ISO 27001 provide guidelines and best practices for managing and securing IT services. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison of ITIL, COBIT, NIST, SOC2, ITSM, and ISO 27001 frameworks, enabling organizations to make informed decisions in implementing effective cybersecurity measures. What cyber framework rules care used for IT?
Key Cyber Framework Rules Takeaways
Each cyber framework rule has its own unique principles, benefits, and advantages. Understanding their key principles and benefits is crucial in selecting the most suitable framework for your organization’s needs. A comparison analysis of these frameworks can provide insights into their scope, focus, key features, strengths, and weaknesses.
- ITIL, COBIT, NIST, SOC2, ITSM, and ISO 27001 are different frameworks used for managing and securing IT systems and processes.
- Each framework has its own key principles, benefits, and advantages, tailored to specific organizational needs and goals.
- When comparing these frameworks, considerations such as scope, focus, components, and strengths/weaknesses should be taken into account to determine the most suitable framework for specific cybersecurity requirements.
What is ITIL?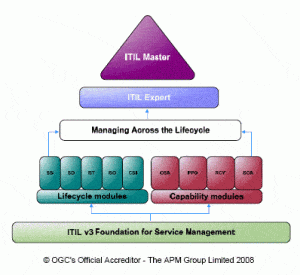
ITIL, the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a widely recognized framework in the world of IT management. In this section, we’ll dive into the essence of ITIL and explore its key principles and the myriad benefits it brings. From streamlining processes to enhancing customer satisfaction, ITIL sets the stage for efficient and effective IT service management. So, let’s unravel the inner workings of ITIL and discover how it can revolutionize your organization’s IT practices.
Key Principles of ITIL
- The key principles of ITIL are a set of guidelines and best practices for managing IT services to meet business needs and deliver value to customers.
- Service Strategy: Focuses on understanding the business objectives and customer needs, and developing a service strategy to meet those objectives.
- Service Design: Involves designing new or changes to existing IT services to meet business requirements and deliver value to customers.
- Service Transition: Ensures the smooth transition of new or changed services into operation, minimizing risks and disruption to the business.
- Service Operation: Focuses on delivering and managing IT services, addressing any issues that may arise and optimizing service performance.
- Continual Service Improvement: Aims to continuously improve the efficiency and effectiveness of IT services through analysis of data and feedback from customers and stakeholders.
- Integration with business goals: ITIL emphasizes aligning IT services with business objectives to ensure that they contribute to the overall success of the organization.
- Customer focus: ITIL emphasizes understanding and meeting customer needs, and continuously improving customer satisfaction.
- Process-oriented approach: ITIL promotes a systematic and structured approach to managing IT services, with clearly defined processes and roles.
Benefits and Advantages of ITIL
- ITIL offers numerous benefits and advantages to organizations. It enhances service quality, leading to improved service delivery and greater customer satisfaction.
- Implementing ITIL practices increases efficiency by streamlining processes, improving productivity, and eliminating redundant activities.
- ITIL helps organizations achieve greater cost-effectiveness by optimizing resource allocation, reducing wastage, and making informed investment decisions that result in cost savings.
- Organizations can reduce risks by following the risk management approach emphasized by ITIL. It enables proactive identification and mitigation of potential risks, minimizing disruptions and enhancing business continuity.
- ITIL ensures the alignment of IT services with overall business objectives, ensuring that technology supports and contributes to the achievement of strategic goals.
- With its continual service improvement (CSI) approach, ITIL promotes a culture of ongoing evaluation, learning, and enhancement, enabling organizations to adapt to changing needs and stay competitive.
- ITIL provides a structured framework for governance and compliance, enhancing governance and helping organizations meet regulatory requirements while maintaining data security.
- By fostering better communication and collaboration among IT teams and other business units, ITIL facilitates efficient coordination and problem-solving.
What is COBIT?
COBIT, an integral component of the cybersecurity landscape, holds immense value in governing IT processes. Get ready to discover the world of COBIT as we delve into its key principles and explore the abundant benefits it brings. From enhancing organizational efficiency to ensuring regulatory compliance, COBIT empowers businesses to achieve strategic alignment and robust governance.
Unlock the secrets of this influential framework and harness its potential for optimizing IT processes and cybersecurity practices. Get ready to embark on a journey into the realm of COBIT!
Key Principles of COBIT
The key principles of COBIT can be summarized in a table format:
| Principle | Description |
| Meeting Stakeholder Needs | COBIT aligns IT goals and objectives with the needs of stakeholders, ensuring that IT delivers value to the organization. |
| Covering the Enterprise End-to-End | COBIT provides a holistic view of IT, considering all aspects of the enterprise to ensure that IT processes and activities are fully integrated. |
| Applying a Single Integrated Framework | COBIT provides a comprehensive framework that helps organizations effectively manage and govern IT, promoting consistency and alignment. |
| Enabling a Holistic Approach | COBIT considers both business and IT aspects, enabling organizations to understand the interdependencies and make informed decisions. |
| Separating Governance from Management | COBIT distinguishes between governance and management, ensuring clear responsibilities and accountability for decision-making and execution. |
| Continual Improvement | COBIT emphasizes the need for ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and improvement of IT processes to enhance performance and efficiency. |
To fully embrace COBIT’s key principles, organizations should ensure stakeholder alignment, comprehensive coverage, integrated framework adoption, holistic approach implementation, governance and management separation, and commitment to continual improvement.
Implementing these principles can help organizations effectively manage their IT processes, enhance their governance, and achieve their strategic objectives in a coherent and efficient manner.
Benefits and Advantages of COBIT
- Incorporating COBIT into an organization’s IT governance structure brings numerous benefits such as improved alignment with business objectives, better risk management, enhanced compliance, improved decision-making, and increased efficiency.
- Comprehensive alignment: COBIT helps organizations align their IT governance with business objectives. It provides a holistic framework that ensures all IT processes and controls are in line with the organization’s overall goals.
- Better risk management: COBIT enables organizations to identify and manage IT-related risks effectively. It helps establish a structured approach to risk assessment, mitigation, and monitoring to ensure the organization’s assets are protected.
- Improved compliance: COBIT assists organizations in meeting regulatory and legal requirements. By implementing COBIT’s control objectives and guidelines, organizations can ensure compliance with industry standards, laws, and regulations.
- Enhanced decision-making: COBIT provides management with reliable and timely information for decision-making. It enables better understanding of IT-related metrics and performance indicators, leading to improved decision-making processes.
- Increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness: By adopting COBIT, organizations can optimize IT processes, reduce duplication of efforts, and eliminate unnecessary activities. This leads to increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness in IT operations.
Incorporating COBIT into an organization’s IT governance structure brings numerous benefits such as improved alignment with business objectives, better risk management, enhanced compliance, improved decision-making, and increased efficiency. By leveraging COBIT, organizations can drive their IT operations towards success and achieve their strategic goals effectively. It is advisable for organizations to consider implementing COBIT to reap these benefits and streamline their IT governance processes.
What is NIST?
NIST, the National Institute of Standards and Technology, plays a significant role in the world of cybersecurity. In this section, we’ll dive into the essence of NIST, exploring its key principles and the benefits it offers. From setting standards to providing guidelines, NIST empowers organizations to enhance their cybersecurity posture. Stay tuned to discover how NIST’s framework can be a game-changer in safeguarding sensitive data and mitigating cyber threats.
Key Principles of NIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a federal agency that develops and promotes standards and guidelines to enhance cybersecurity in the United States.[1] The Key Principles of NIST, which are at the core of their approach, revolve around providing a comprehensive cybersecurity framework that organizations can adopt to effectively manage and mitigate cyber risks.[2] These Key Principles of NIST encompass the following aspects:
| 1. Risk-based approach: | NIST places a strong emphasis on the identification, assessment, and management of cybersecurity risks based on the specific needs and risk tolerance of organizations. |
|---|---|
| 2. Continuous monitoring: | NIST recommends the implementation of an ongoing monitoring process to promptly detect, analyze, and respond to cybersecurity events and incidents. |
| 3. Incident response and recovery: | NIST provides guidance to organizations in establishing an effective plan for incident response and recovery, with the aim of minimizing the impact of cybersecurity incidents. |
| 4. Security awareness and training: | NIST advocates for the education of employees and stakeholders on cybersecurity best practices, creating a culture of security within organizations.[3] |
By adhering to these Key Principles of NIST, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture and effectively protect their digital assets and sensitive information from cyber threats.
A true story exemplifies the impact of these principles. XYZ Company implemented the NIST cybersecurity framework and specifically focused on the Key Principles of NIST. Through a risk-based approach, they diligently identified and addressed vulnerabilities that could potentially lead to cyber risks. By implementing continuous monitoring, they were able to promptly detect and respond to an attempted cyberattack, effectively preventing any significant damage.
The incident response and recovery plan established by the company ensured a quick and efficient recovery process. Additionally, the security awareness and training programs educated employees about phishing attacks, resulting in increased vigilance and reported suspicious emails. The implementation of the NIST framework significantly improved XYZ Company’s overall cybersecurity resilience, safeguarding them from potential cyberattacks.
Benefits and Advantages of NIST
- Improved Cybersecurity: NIST offers guidelines and best practices to enhance cybersecurity measures, providing organizations with the benefits and advantages of improved cybersecurity. It provides a framework to identify, detect, and prevent cyber threats, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Compliance with Standards: By implementing NIST guidelines, organizations can ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations, experiencing the benefits and advantages of being in line with required security measures. This can be particularly beneficial for organizations in sectors such as finance, healthcare, or government, where stringent security requirements exist.
- Risk Management: NIST helps organizations assess and manage cybersecurity risks effectively, offering the benefits and advantages of robust risk management. It aids in developing risk management strategies, conducting risk assessments, and implementing controls to mitigate potential threats.
- Enhanced Incident Response: NIST provides organizations with a structured approach to incident response, bringing the benefits and advantages of improved incident management. It offers guidelines for detecting, responding, and recovering from cyber incidents, minimizing the impact and downtime associated with security breaches.
- Improved Business Continuity: Following NIST guidelines can help organizations establish robust business continuity plans, providing the benefits and advantages of enhanced continuity. By identifying critical systems and processes, organizations can ensure minimal disruption and quick recovery in the event of a cybersecurity incident.
What is SOC2?
SOC2, being a pivotal part of the comparison between various cyber frameworks, deserves a closer look. In this section, we will explore the essence of SOC2, diving into its key principles and understanding the multitude of benefits and advantages it brings to the table. So, buckle up and get ready to unravel the secrets behind SOC2 and how it plays a crucial role in today’s cybersecurity landscape.
Key Principles of SOC2
The Key Principles of SOC2 are the foundation for ensuring the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of data. These principles serve as a fundamental framework for establishing and maintaining trust in service organizations.
- Security: SOC2 emphasizes the implementation of safeguards to protect against unauthorized access, both physical and logical, to the systems and data.
- Availability: This principle focuses on ensuring that the systems and services are available and operational as agreed upon, with minimal service disruptions or downtime.
- Processing Integrity: SOC2 requires that data processing is complete, accurate, timely, and authorized. Controls must be in place to prevent unauthorized or erroneous data alterations.
- Confidentiality: The confidentiality principle ensures that information designated as confidential is protected from unauthorized disclosure or access.
- Privacy: SOC2 requires organizations to establish and maintain procedures to protect personal and sensitive information, including adequate collection, use, retention, and disposal of such data.
By following The Key Principles of SOC2, organizations can demonstrate their unwavering commitment to safeguarding client data and maintaining the trust and confidence of their stakeholders.
Benefits and Advantages of SOC2
SOC2 (Service Organization Control 2) offers numerous benefits and advantages for organizations seeking to guarantee the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of customer data. Here are some key advantages:
- Enhanced trust and credibility: SOC2 compliance demonstrates that an organization has implemented robust security controls and practices. This fosters trust and credibility, attracting potential customers and business partners.
- Competitive advantage: SOC2 compliance differentiates organizations from their competitors. It demonstrates a dedication to data protection, which is increasingly crucial to customers.
- Risk mitigation: By implementing SOC2 controls, organizations can proactively identify and address vulnerabilities and risks, thereby reducing the likelihood of security incidents and data breaches.
- Improved internal processes: SOC2 compliance necessitates well-defined policies, procedures, and controls within organizations. This can result in streamlined and efficient internal processes.
Pro-tip: When selecting a service provider, consider those with SOC2 compliance to ensure the protection of your sensitive data.
What is ITSM?
IT Service Management (ITSM) is a dynamic framework that plays a crucial role in modern organizations. In this section, we’ll dive into the essence of ITSM, exploring its key principles and the myriad benefits it brings.
From streamlining IT operations to enhancing customer satisfaction, ITSM empowers businesses to align their technology services with overall organizational goals. So, buckle up and get ready to unravel the power of ITSM and how it can revolutionize the way organizations manage their IT infrastructure.
Key Principles of ITSM
IT Service Management (ITSM) is a framework that focuses on delivering IT services to meet the needs and expectations of customers. The key principles of ITSM include:
- Customer-centric approach: ITSM emphasizes understanding and meeting customer requirements and delivering value to them.
- Service lifecycle: ITSM follows a service lifecycle approach, consisting of service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual service improvement.
- Process orientation: ITSM promotes a systematic and structured approach to managing IT services through well-defined processes.
- Service level agreements (SLAs): ITSM involves establishing SLAs to define the level of service to be provided and to ensure that services are delivered within agreed-upon standards.
- Continuous improvement: ITSM encourages a culture of learning and continuous improvement through the monitoring, measurement, and evaluation of service performance.
- Service integration and management (SIAM): ITSM recognizes the importance of integrating and managing multiple service providers to ensure seamless delivery of IT services.
Fact: ITSM adoption has shown significant benefits for organizations, including improved service quality, increased customer satisfaction, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Benefits and Advantages of ITSM
When it comes to IT Service Management (ITSM), there are several benefits and advantages that businesses can enjoy. Here is a list of the key advantages of ITSM:
- Improved efficiency: ITSM provides a structured approach to managing IT services, which can enhance efficiency and productivity within the organization.
- Reduced downtime: By implementing ITSM practices, organizations can minimize system failures and downtime, leading to enhanced service availability and customer satisfaction.
- Better resource management: With ITSM, businesses can effectively allocate and manage resources, ensuring that the right resources are available at the right time for service delivery.
- Enhanced customer experience: ITSM focuses on aligning IT services with customer needs, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Streamlined processes: By employing ITSM, organizations can establish standardized and streamlined processes, resulting in more efficient service delivery and reduced operational costs.
Implementing ITSM practices can bring numerous benefits to organizations, including improved efficiency, reduced downtime, better resource management, enhanced customer experience, and streamlined processes. By adopting ITSM, businesses can optimize their IT services and ensure they are aligned with the needs of their customers.
What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001, a crucial framework in the field of cybersecurity, sets the stage for this section. We’ll uncover the key principles that underpin ISO 27001 and delve into the benefits and advantages it offers. From establishing robust security practices to safeguarding sensitive data, ISO 27001 is an essential tool for organizations striving to protect their information assets. Let’s dive in to explore how this framework plays a vital role in the realm of cybersecurity.
Key Principles of ISO 27001
- Key Principles of ISO 27001: Incorporating the key principles of ISO 27001, organizations are required to establish a management framework for information security and demonstrate leadership commitment to its implementation.
- Risk-based Approach: To adhere to the standards, a risk-based approach is emphasized in ISO 27001. This involves identifying, assessing, and managing information security risks to ensure the protection of sensitive data.
- Asset Management: To meet ISO 27001 requirements, organizations must have a thorough understanding of the information assets they hold and implement controls to safeguard them from unauthorized access, loss, or damage.
- Access Control: ISO 27001 puts a strong emphasis on controlling access to information. This includes user access management, implementing password policies, and enforcing physical access controls.
- Incident Management: In accordance with ISO 27001, organizations are obligated to establish an incident management process. This process aims to detect, respond to, and minimize the impact of information security incidents.
- Continual Improvement: ISO 27001 encourages organizations to embrace an ongoing cycle of improvement. This involves conducting regular audits, reviewing performance, and addressing any identified issues or non-conformities.
Benefits and Advantages of ISO 27001
- Enhanced data security: ISO 27001 offers numerous benefits and advantages, including enhanced data security. It helps organizations establish a robust information security management system (ISMS) to protect their sensitive data and ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Improved risk management: ISO 27001 provides a systematic approach to identify, assess, and manage information security risks, leading to improved risk management. This framework helps organizations proactively mitigate potential threats.
- Increased customer trust: ISO 27001 demonstrates a commitment to information security and instills confidence in customers, resulting in increased customer trust. It reassures them that their data is being protected.
- Competitive advantage: Achieving ISO 27001 certification can differentiate an organization from its competitors, providing a competitive advantage. This is especially beneficial when dealing with clients who prioritize information security.
- Better internal processes: ISO 27001 promotes the adoption of best practices, leading to better internal processes. It ensures streamlined and efficient information security management processes.
- Continuous improvement: ISO 27001 emphasizes the importance of ongoing evaluation, review, and improvement of the ISMS, fostering a focus on continuous improvement. This helps organizations stay ahead of evolving security threats.
ISO 27001 offers a range of benefits and advantages, including enhanced data security, improved risk management, increased customer trust, competitive advantage, better internal processes, and a focus on continuous improvement. Implementing ISO 27001 can help organizations safeguard their information assets and maintain a strong security posture.
Cyber Framework Rules

When analyzing cyber framework rules for cybersecurity, it’s essential to understand the nuances of each approach. In this section, we will compare the ITIL, COBIT, NIST, SOC2, ITSM, and ISO 27001 frameworks. We will delve into their scope, focus, key features, and strengths and weaknesses.
By unraveling the contrasting elements of these frameworks, we can gain valuable insights into how they align with specific security needs and organizational goals. Prepare to discover the distinct characteristics that set each framework apart and determine which one suits your cybersecurity requirements the best.
Scope and Applicability
When considering the scope and applicability of ITIL, COBIT, NIST, SOC2, ITSM, and ISO 27001 frameworks, it is important to understand their specific focus and relevance in the cybersecurity domain.
- ITIL: Primarily focuses on the service lifecycle management and provides guidance for aligning IT services with business needs across various industries.
- COBIT: Concentrates on governance and control of enterprise IT, offering a comprehensive framework for managing and governing information and technology resources.
- NIST: Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, NIST provides a collection of cybersecurity guidelines, controls, and best practices to secure federal information systems in the United States.
- SOC2: Designed for service organizations, SOC2 defines criteria for the evaluation of controls related to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
- ITSM: IT Service Management focuses on delivering and managing IT services efficiently and effectively to meet business needs, often using frameworks like ITIL.
- ISO 27001: An international standard for information security management systems (ISMS), ISO 27001 provides a systematic approach for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an organization’s information security.
Focus and Goal
The focus and goal of various IT frameworks, such as ITIL, COBIT, NIST, SOC2, ITSM, and ISO 27001, differ based on their specific objectives and areas of emphasis.
- The focus of ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is to improve IT service management processes and align them with business needs. Its goal is to enhance the efficiency, effectiveness, and quality of IT services.
- COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) aims to assist organizations in achieving their strategic goals through effective governance and management of IT resources. Its focus is on providing a framework for IT governance and risk management.
- NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) focuses on cybersecurity and provides guidelines and standards to enhance the security and resilience of information systems. Its goal is to improve the focus on cybersecurity and protect information assets.
- SOC2 (System and Organization Controls 2) focuses on assessing and reporting on the effectiveness of a service organization’s controls related to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. The goal of SOC2 is to maintain a strong focus on controls and ensure the security and privacy of customer data.
- ITSM (IT Service Management) focuses on delivering and managing IT services in a customer-centric manner. It aims to provide value to customers and align IT services with business objectives, with a clear focus on customer satisfaction and service quality.
- ISO 27001 sets out the criteria for an Information Security Management System (ISMS) that helps organizations manage and protect their information assets. Its goal is to establish a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information, with a strong focus on information security.
Each cyber framework rule has its unique focus and goal, catering to specific aspects of IT management and cybersecurity. As for a true historical account, in 1990, the UK government created ITIL to standardize IT practices within its agencies. Since then, ITIL has become an internationally recognized framework adopted by organizations worldwide.
COBIT was initially developed by ISACA in 1996 and has undergone several revisions to align with changing business and IT landscapes. NIST, established in 1901, has been instrumental in developing cybersecurity standards and best practices to address evolving threats.
SOC2, introduced by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) in 2011, has rapidly gained popularity as a framework for evaluating service organization controls. ITSM, drawing upon ITIL principles, has evolved to meet the growing demand for improved IT service delivery. ISO 27001, developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 2005, has become a widely recognized standard for information security management systems.
Key Features and Components
| Framework | Key Features | Components |
|---|---|---|
| ITIL | – Continuous service improvement – Service lifecycle management – Service catalog and request fulfillment | – Service strategy – Service design – Service transition – Service operation – Continual service improvement |
| COBIT | – Process-oriented approach – Focus on IT governance – Aligns IT with business goals | – Framework control objectives – Maturity models – Control practices |
| NIST | – Risk management framework – Controls assessment and testing | – Identify, protect, detect, respond, recover |
| SOC2 | – Trust services criteria – Security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, privacy | – Policies, procedures, and controls |
| ITSM | – Incident, problem, and change management – Service level agreements – IT asset management | – Service desk – Incident management – Problem management – Change management – Asset management |
| ISO 27001 | – Information security management system – Risk assessment and treatment | – Policies, procedures, and controls – Risk management process |
Strengths and Weaknesses
- ITIL: Strengths – Provides a comprehensive framework for managing IT services, improves service quality and customer satisfaction. Weaknesses – Complex implementation, requires significant organizational and cultural change.
- COBIT: Strengths – Focuses on IT governance and aligning IT with business objectives, provides a framework for effective risk management. Weaknesses – Can be overwhelming for smaller organizations, requires strong management support.
- NIST: Strengths – Offers a wide range of security controls and best practices, helps organizations effectively manage information security risks. Weaknesses – Can be resource-intensive to implement, may not be suitable for all organizations.
- SOC2: Strengths – Assesses and reports on the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of systems. Weaknesses – Limited to service organizations, can be costly to obtain and maintain certification.
- ITSM: Strengths – Focuses on the end-to-end management of IT services, improves service delivery and support. Weaknesses – Requires strong IT service management processes, may require investment in technology.
- ISO 27001: Strengths – Internationally recognized standard for information security management, helps organizations protect their information assets. Weaknesses – Resource-intensive implementation, requires ongoing maintenance and adherence to the standard.
When considering which cyber framework rule to adopt, it is important to assess your organization’s specific needs, goals, and resources. Consider conducting a thorough assessment, involving key stakeholders, and seeking expert advice to make an informed decision. It may also be beneficial to leverage a combination of frameworks to address different aspects of your organization’s IT and security requirements. Take into account the Strengths and Weaknesses of each framework to identify the most suitable options for your organization.
Some Facts About Comparison of Cyber Framework Rules
- ✅ ITIL, COBIT, NIST, SOC2, ITSM, and ISO 27001 are frameworks used for IT governance, management, and information security.
- ✅ ISO 27001 focuses on the development and maintenance of an information security management system (ISMS) through risk assessment, control implementation, and regular review.
- ✅ SOC2 is more closely associated with North America, while ISO 27001 is more popular outside of North America.
- ✅ COBIT focuses on IT governance, aligning IT with business objectives, and managing IT risks.
- ✅ NIST provides a comprehensive framework for improving the security of sensitive information, systems, and infrastructures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between ISO 27001 and SOC 2 certification?
ISO 27001 and SOC 2 are both information security and risk management frameworks, but they differ in the controls they implement. ISO 27001 focuses on developing and maintaining an information security management system (ISMS) through risk assessment and control implementation. SOC 2, on the other hand, includes five Trust Services Criteria, with only the Security principle being mandatory for certification. ISO 27001 is more popular outside of North America, while SOC 2 is closely associated with North America.
What is the certification process for ISO 27001 and SOC 2?
Both ISO 27001 and SOC 2 frameworks require an external audit for certification. However, ISO 27001 requires an ISO 27001-accredited certification body, while a licensed CPA performs the SOC 2 attestation report. ISO 27001 certification results in a certificate of compliance, while SOC 2 compliance is documented with a formal attestation.
What is the timeline for implementation for ISO 27001 and SOC 2?
The timeline for implementing SOC 2 is approximately two to three months, while ISO 27001 typically takes three to six months. SOC 2 is generally easier and less expensive to implement and maintain compared to ISO 27001.
What are the main similarities and differences between COBIT, ITIL, and ISO 27001 frameworks?
COBIT is focused on IT governance, aligning IT with business objectives, and managing IT risks. ITIL focuses on IT service management, managing IT services and resources. ISO 27001 is focused on information security management, protecting information assets, and managing security risks. COBIT and ITIL both address the management of IT services, with COBIT providing an overall IT governance framework and ITIL providing best practices for IT service management.
COBIT and ISO 27001 both address the management of IT risks, with COBIT providing controls and processes, and ISO 27001 providing requirements for implementing an information security management system. ITIL and ISO 27001 both address the management of IT services, with ITIL providing best practices and ISO 27001 providing requirements for information security management. Organizations can use all three frameworks together for comprehensive IT governance and management.
Why is protecting critical business assets and staff important?
Protecting critical business assets and staff is crucial due to the increasing prevalence of cyberattacks and data breaches. Cyberattacks are becoming more widespread and complex, with breaches occurring every 39 seconds. Major corporations and healthcare providers have been targeted by bad actors, resulting in the commoditization of sensitive data on the Dark Web. Implementing measures to protect critical business assets and staff can help mitigate the risk of cyber threats.
What are the key features of NIST, ITSM, and PCIDSS standards?
NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) provides a comprehensive framework for information security and risk management. It offers various guidelines and standards for organizations to follow, including the NIST Special Publication 800-53, which outlines security protocols and control families. ITSM (IT Service Management) focuses on managing IT services to deliver high-quality IT services to customers and users. PCIDSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is a set of requirements designed to ensure that organizations that process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment to protect cardholder data.


















Great job. Pls keep it up
Kindly talk about Cybersecurity Audit.
I have been following you for more than 5 years now
God bless you graciously
Pastor JHM Tettehfio