What Is Lean Waste?
Are you working harder these days or working smarter, and how do you know the difference? Many of the reasons we end up working so hard — and not so smart — have to do with our failure to recognize the obstacles that get in our way and waste our precious time. We may just have the wrong paradigm. The focus in a lean thinking paradigm is to eliminate the obstacles, lean waste, or muda (the Japanese word for “waste”). So, what is lean waste?
Lean Thinking Paradigm
The lean thinking paradigm is constantly looking for the obstacles in our way that are impeding a smooth flow of work. The obstacle that cause us to work harder to overcome instead of working on eliminating them in the first place.
Working Harder Because of Waste
In our western culture, our values influence the organizational design. The harder we work, the better we feel. The only problem with this mentality is that working harder does not necessarily translate into working more productively. In other words, the goal is producing results, and working hard does not always translate into results. To produce results, we need to work smarter, not harder. There is an easy way to tell the difference between working harder and working smarter.
The symptoms of working harder include:
- Working more than 40 hours a week (overtime);
- Struggling to meet deadlines;
- Juggling multiple projects to get more done;
- Reworking/editing/repairing your projects to make them better;
- Wasting valuable time on “non-value-added” activities; and
- Asking for more resources (time, money, people, or equipment) to solve a problem.
We all work hard to some degree. We are pressed for time, so we take work home, yet we still struggle to meet deadlines as we rush from project to project. What is going on? Well, the biggest waste of all is that we are underutilizing our brains to solve the problem. We need information, knowledge, and wisdom to be efficient. Working harder will not resolve the chaos. The only way to reduce the chaos in our lives is to work smarter, not harder.
Lean is about Working Smarter
Working smarter requires that we understand the obstacles that get in our way, wasting precious time, like the lean waste that occurs in our organizations.Value stream maps are a tool used to visualize the process and classify each step as valuable (green dot), waste (red dot), or required non-value added (black dot) steps in the process. In this way the we learn to see the waste, uncovering the hidden waste so that it becomes more obvious.
We have to create a system to eliminate the waste in a continuous manner. In a lean organization it is the objective and responsibility of process improvement or the quality system (as in ISO compliance) to identify and eliminate all wasted activity.
The rewards of working smarter include:
- Going home on time to see your family;
- Completing all assigned work and meeting your deadlines;
- Focusing on one project at a time;
- Getting your work done right the first time;
- Working only on value added activities; and
- Getting more done with fewer resources.
Working smarter releases tremendous amounts of capacity within your organization – capacity that you did not realize you had. By working smarter, it is not unrealistic to find that you can accomplish 100% more work with the same resources. If you continue to work at it, you can increase your capacity again for a 300% or more increase. That is the real power of business process management.
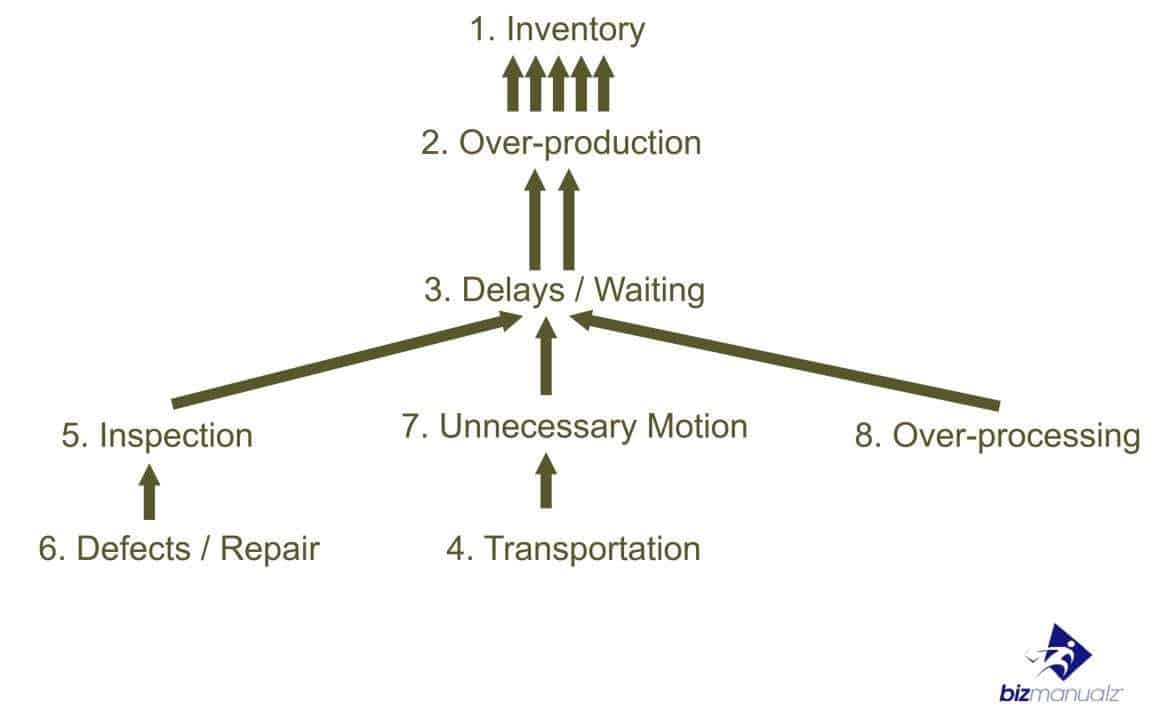
The Eight Categories of Lean Waste (Muda)
Just what does this lean waste look like?
1. Unnecessary Inventory
It all start with too much inventory. Maintaining excess inventory, supplies, work in process (WIP), or finished goods in order to compensate for process inaccuracy or the other mudas. Too much Inventory is the most obvious sign or symptom of waste somewhere.
2. Overproduction
Manufacturing of products before they are needed or processing of unnecessary information, (i.e. forms or data that are not needed).
3. Idle Time, Waiting or Delays
Idle time spent waiting for something (tools, supplies, parts, or information). In today’s economy, all information (money is a form of information) should be communicated instantaneously. Delays mean that the potential for improvement is obvious and (in absence of regulation) should be easy.
4. Under-utilizing Employees, Oversight or Inspection
Not using the full productive capacity of all employees creativity and thinking power. Having one worker (a supervisor, inspector, or manager) watch another worker do his job. If a worker cannot be trusted to do a job, an efficient enterprise retrains or replaces the worker, or redesigns the task. Having one worker (a manager) inspect the work of another after it has been completed. A worker capable of performing the task should be competent to determine whether it is up to standards.
5. Defects, Correction, Repair or Rework
Design of goods that do not meet customer needs. Performing the same task a second time, rescheduling, and capacity losses. Any mistake correction activity. We should strive to do it right the first time!
6. Unnecessary Motion
Not focusing on ergonomic design. Any wasted motion to pick up parts or stack parts. Any wasted walking or moving around. Wasting time looking for things in a cluttered work space or desk. Not being organized;
7. Unnecessary Transporting, Conveyance or Movement
Unnecessary movement of products, people, or information. Transporting materials, parts or finished goods into or out of storage (inventory) or between processes.
8. Unnecessary Processing
Over-processing occurs when one tries to provide higher quality or extra operations than are necessary to meet the customer’s needs. Using more expensive equipment or tools where simpler ones would suffice. Having meetings or people at meetings that are not needed.
Lean and Services
The concept of “lean” was developed for production environments but with a few modifications, it applies to services as well. In either case, Lean considers the use of resources for goals other than “creating value for the customer” to be waste and such wastes should be eliminated.
From the customer’s perspective, value describes an item or a service they’re willing to pay for. Lean is sometimes said to be about “creating more value with less work”; in reality, it’s about “maximizing value while minimizing waste”. And though people can’t seem to agree on much of anything in the health care “debate”, one thing we should all be able to agree on is that there’s plenty of inefficiency throughout the health care system.
Bicheno and Holweg (in their book, “Lean Toolbox”), describe seven service wastes:
- Delay – customers waiting for a service;
- Duplication – having to reenter data, repeat details on forms, copy information across, or answer queries from several sources within the same organization;
- Unnecessary Movement – having to get in line several times, lack of a “one-stop” service encounter, etc.;
- Unclear Communication – wastes of seeking clarification, confusion over product or service use, wasting time finding a location that may result in misuse or duplication;
- Incorrect inventory – being out-of-stock, unable to get exactly what was required, substitute products or services, or not having the right provider available;
- Opportunity lost to retain or win customers – failure to establish rapport, ignoring customers, unfriendliness, and rudeness; and
- Errors in the service transaction – product defects in the product-service bundle, lost or damaged goods (famously, the airman who was supposed to have his gallbladder removed but had his lower limbs amputated).
Think Lean is Impossible?
As providers and as customers, we’ve seen these wastes…far too many times. We need to remove as many of these wastes as possible and improve the process. That’s where Lean can help, and many health care providers are already implementing Lean and other process improvement tools and techniques.
Now that you know about lean waste, you need to learn more about how to use process improvement programs to work smarter in your organization by attending our upcoming classes.















Leave a Reply