What Are The Five Stages of Process Improvement?
Process improvement is essential for an organization’s growth and success. It includes analyzing processes, finding areas to improve, making changes, and monitoring results to ensure progress. The five stages of process improvement provide a structured approach to achieve this goal. What are the five stages of process improvement?
Preparing Five Stages of Process Improvement
DMAIC is an acronym representing the key phases of the Six Sigma methodology: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It’s a systematic approach for process improvement.
- Stage one: define the process. The problem and project goals are established. Understanding the current process, including its inputs, outputs, and activities key. This helps to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies that need to be tackled.
- Stage two: measure performance. It involves data collection to understand the current process performance. Start by gathering data on key metrics, like cycle time, defect rate, and customer satisfaction. These measurements can be used for future improvements, and to identify areas that need attention.
- Stage three: analyze data. Look for patterns, trends, and root causes that could hinder performance. Use tools like histograms or cause-and-effect diagrams to gain valuable insights.
- Stage four: improving the process. It focuses on implementing changes for better performance. Test possible changes or modifications, and involve key players to ensure successful implementation.
- Stage five: controlling and sustaining improvements. Monitor effectiveness and make adjustments if needed. Keeping track ensures any issues are addressed before they become major hurdles.
DMAIC is widely used in industries to enhance processes, reduce defects, and achieve higher quality, making it a valuable tool for continuous improvement and problem-solving. To make these stages more effective, consider these suggestions:
- Encourage employee input to create a culture of continuous improvement.
- Use technology, like automation and data analytics tools, to streamline processes and improve accuracy.
- Establish KPIs to measure the success of process improvements, and find areas to enhance.
By following these suggestions, organizations can create an environment for process improvement and achieve long-term growth. A systematic approach and commitment to evaluation helps organizations stay ahead of their competition and deliver great results.
The importance of process improvement
Process improvement is pivotal for boosting organizations’ efficiency and productivity. Companies can refine existing processes, reduce costs and offer better products/services. Here are 5 reasons why it’s so important:
- Enhanced operational efficiency – identify bottlenecks and remove unnecessary steps, for smoother workflows and higher productivity.
- Cost reduction – optimize processes to find underused/wasted resources, leading to savings.
- Improved quality – detect defects early and prevent them, for better outcomes.
- Better customer satisfaction – streamlined processes mean faster response times, fewer errors and improved customer service.
- Competitive advantage – by staying ahead of trends and quickly adapting, companies gain an edge by delivering value to customers.
Continuous improvement is key for long-term success. Organizations should foster an environment where employees contribute ideas and collaborate to reach excellence.
To illustrate the importance of process improvement, here’s a real-life story: A manufacturing company was delayed due to complex production processes. Through analysis and collaboration, they removed redundant steps and shortened production time by 30%. This enabled them to meet deadlines, and increase customer satisfaction.
Process improvement is essential for successful businesses. Organizations can use it to drive growth, innovation and success in today’s competitive landscape.
Stage 1: Identifying current processes
To kickstart your journey in Stage 1: Identifying current processes, delve into the world of assessing the efficiency and effectiveness of your existing processes. Additionally, gather valuable data and feedback from stakeholders. These sub-sections will serve as your solutions to gaining insights and understanding the current state of your processes.
Assessing the efficiency and effectiveness of current processes
Analyzing performance is vital for evaluating efficiency and effectiveness of current processes. This enables organizations to spot areas for improvement, and make wise decisions to increase productivity and effectiveness.
Not just the quantitative elements, but also the qualitative features must be taken into account when judging efficiency and effectiveness. These may include customer satisfaction, employee morale, and overall business impact.
Throughout time, organizations have perpetually attempted to refine their processes by assessing their efficiency and effectiveness. By recognizing strengths and weaknesses, companies have implemented changes for growth and better outcomes.
Gathering data and feedback from stakeholders
Gathering data and feedback from stakeholders is possible by using several methods. Surveys, interviews, focus groups, analyzing existing documentation or data – these are all options. With these interactions, organizations can find out what stakeholders think of current processes, distinguish issues that need to be fixed and get advice on how to change them.
A top tip: To make sure stakeholders give honest answers, you should create an environment that is both safe and inclusive. Offering anonymity in surveys and confidentiality in interviews can motivate people to participate.
Stage 2: Analyzing and mapping processes
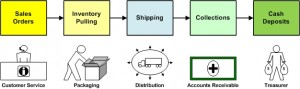
Revenue Process Map
To analyze and map processes in Stage 2 of process improvement, utilize the following sub-sections as solutions: Identifying bottlenecks and areas for improvement, and Creating process flowcharts and diagrams.
These approaches will enable you to uncover inefficiencies, pinpoint areas needing enhancement, and visually depict the sequence of activities for optimal process understanding.
Identifying bottlenecks and areas for improvement
A manufacturing company had a problem – production delays. To identify the bottleneck, they took action! They examined data flow, asked employees for feedback, simulated processes and checked KPIs against industry standards.
They found the issue – a malfunctioning machine. And what did they do? Invested in upgrading it and implementing preventive maintenance measures. This improved production time, resulting in increased output and customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, identifying bottlenecks and areas for improvement helps organizations optimize processes, reduce costs, and deliver better products or services.
Creating process flowcharts and diagrams
Flowcharts and diagrams are essential for understanding complex processes. Symbols such as arrows, rectangles, diamonds, and circles can be used to show different actions, decisions, inputs, and outputs.
Through visuals, one can better comprehend how each step relates to the overall goal. This helps to pinpoint areas that need improvement or optimization.
Diagrams provide an overview of the whole process. This helps to show any interdependencies between different subprocesses or tasks.
Creating these visuals is also useful for communication. The visuals act as a ‘common language’ which everyone involved can easily understand.
I experienced this first-hand. On one project, there were delays due to miscommunication. So, we made flowcharts and diagrams of the workflow. This helped us identify communication gaps and coordinate effort better. So, the product was delivered on time and with improved efficiency.
Visuals are very powerful for optimizing processes within an organization.
Stage 3: Implementing process changes
To implement process changes effectively in Stage 3, “Implementing process changes,” focus on developing a plan for implementing process improvements and effectively communicating these changes to relevant stakeholders. These sub-sections will provide you with solutions to ensure a seamless transition and successful integration of process improvements.
Developing a plan for implementing process improvements
To implement process improvements, detail and collaboration are key. Anticipating potential challenges is a must – so it’s wise to devise contingencies to minimize disruption.
Take a manufacturing company as an example. They analyzed their production line and decided to automate. To make this happen, they created a plan that included:
- Employee training programs
- Investing in modern machinery
- Setting up performance monitoring systems
The implementation was successful – leading to cost savings, reduced lead time and improved quality.
Communicating changes to relevant stakeholders
Start off by stating why the changes are necessary. This will help stakeholders comprehend why it is needed and earn their backing.
Be candid about how the changes will affect different stakeholders. Attend to their hesitations and make sure their voices are heard during the entire process.
Pick the ideal communication outlets to reach each stakeholder group correctly. Make your messages pertinent to their individual needs and inclinations.
Issue regular updates on the progress of the implementation process. This will keep stakeholders educated and engaged, helping them feel appreciated and engaged.
Moreover, it’s essential to sustain an open dialogue with stakeholders constantly. By attentively listening to their feedback and tackling any issues rapidly, you can generate trust and ensure a smooth transition.
Let me tell you a real story that illustrates how significant effective communication is during a process change. In a major multinational company, there was opposition from employees when a fresh performance management system was launched.
The leadership team noticed they hadn’t adequately communicated the purpose and advantages of this transformation. They quickly organized town hall meetings, held one-on-one sessions with employees, and gave thorough training on how to use the new system.
By involving employees in these communication efforts actively, they managed to transform skepticism into enthusiasm and successfully implemented the new process.
Remember, efficient communication is essential when applying process changes, as it guarantees stakeholders are informed and committed to achieving favourable outcomes.
Stage 4: Monitoring and measuring process performance
To effectively monitor and measure process performance in Stage 4: Monitoring and measuring process performance, you need to establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and collect data while analyzing performance metrics. These sub-sections provide solutions to track and evaluate the effectiveness of your process improvement efforts.
Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs)
KPIs are essential for tracking and measuring process performance. They’re quantifiable metrics that indicate success. To measure their social media campaigns, a digital marketing agency could use KPIs like engagement rate, click-through rate, and conversion rate.
This table illustrates how to calculate them:
| Metric | Definition | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement Rate | The percentage of followers who interact with content by liking, commenting, or sharing it | Number of interactions / Total followers |
| Click-through Rate | The percentage of users who click on a link in a post to visit a website or landing page | Clicks on link / Total impressions |
| Conversion Rate | The percentage of visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form | Number of conversions / Number of visitors |
Engagement rate shows audience interest, click-through rate measures traffic, and conversion rate indicates lead generation and customer acquisition. To optimize campaigns, organizations should analyze these KPIs. This helps to identify areas for improvement, spot trends, and take timely action that aligns with goals.
Don’t miss out! Establishing KPIs is a great way to maximize process performance. It provides a roadmap to success and enables data-driven decisions to boost efficiency, productivity, and business growth. Start today and set meaningful KPIs that drive your organization.
Collecting data and analyzing performance metrics
Organizing data? A table is a great way to go. Check this out:
| Metric 1 | Metric 2 | Metric 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Process A | 10 | 5 | 8 |
| Process B | 8 | 7 | 6 |
| Process C | 9 | 9 | 7 |
Digging deeper? Yes, please! Analyzing performance metrics regularly can uncover trends and patterns that could be hidden in long-term reports.
Here’s an example:
Once upon a time, in a multinational company, the manufacturing department was facing productivity issues. But data analysis of production metrics revealed a fault with one machine. Fixing it quickly led to improved efficiency and profits.
Data collection and performance metrics analysis are key stages in monitoring process performance. It helps organizations make informed decisions, fix what needs fixing and keep growing.
Stage 5: Continuously improving processes
To continuously improve processes in Stage 5, encourage a culture of continuous improvement and learn from past experiences for implementing iterative changes.
Encouraging a culture of continuous improvement
Establishing clear goals and objectives encourages continuous improvement. When employees understand what they’re working for and why it matters, they’re more likely to innovate. Don’t forget to communicate these goals and provide feedback to keep everyone aligned and motivated.
Creating a safe space for experimentation and taking risks is also key. Encourage employees to explore without the fear of failure. Celebrate successes and failures as learning experiences – that way, continuous improvement will be part of the company’s DNA.
Invest in employees’ professional development by providing resources such as training programs and tools. This empowers them to take ownership of their growth. Show your commitment to continuous learning by investing in employees’ development.
Learning from past experiences and implementing iterative changes
To really learn from past experiences, consider what hasn’t been explored yet. Delve into details to find tailored strategies.
Encourage open communication! Ideas and perspectives should be welcomed. Insights can lead to innovations.
Risk-taking is key! Allow room for trial and error. Failure is an opportunity for growth.
These approaches create an environment where processes evolve and thrive. Open comms, experimentation and risk-taking all drive continuous improvement.
Five Stages of Process Improvement
In the end, the five stages of process improvement are very important for increasing organizational efficiency and effectiveness. Each stage helps to make operations smoother, reduce costs, and increase customer satisfaction.
To get started, organizations must thoroughly assess and analyze their existing processes. This initial step helps to recognize places to improve and set goals that are achievable. By doing research and data analysis, organizations can gain understanding of their current practices and create plans to improve them.
The next stage is designing and applying changes from the assessment phase. It’s essential to involve key people at this stage to make sure everyone agrees and works together. With careful planning and communicating the changes, resistance and disapproval can be kept to a minimum.
During implementation, it’s important to watch the progress of the changes and fix any problems that come up. This proactive way lets for adjustments right away and keeps the process improvement project going.
Once the changes are in place, organizations should always evaluate how well they are reaching desired outcomes. Checking key performance indicators (KPIs) enables continuous measurement of success and noticing areas that need more work.
To make sure improvements last, organizations need to promote continuous improvement. This means motivating employees to look for chances to enhance things and share new ideas. By giving people responsibility and being held accountable, process improvement will become part of the overall business strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
 FAQ 1: What are the five stages of process improvement?
FAQ 1: What are the five stages of process improvement?
Answer: The five stages of process improvement are:
1. Define: This stage involves clearly defining the objectives, scope, and boundaries of the process to be improved.
2. Measure: In this stage, the current state of the process is measured using relevant metrics and data to identify areas of improvement.
3. Analyze: The measured data is analyzed to identify root causes, bottlenecks, and areas where improvements can be made.
4. Improve: This stage focuses on implementing the identified improvements and solutions to optimize the process.
5. Control: The final stage ensures that the improved process is monitored, controlled, and sustained over time.
FAQ 2: Why is defining the process important in process improvement?
Answer: Defining the process is important in process improvement because it sets clear objectives, scope, and boundaries. This helps in identifying potential issues, understanding the inputs and outputs, and determining the stakeholders involved. Without a clear definition, it becomes difficult to measure, analyze, and improve the process effectively.
FAQ 3: How does the measurement stage contribute to process improvement?
Answer: The measurement stage is crucial in process improvement as it provides data and metrics to assess the current state of the process. This data helps in identifying areas of improvement, measuring the effectiveness of implemented changes, and tracking progress. It allows for informed decision making and validation of improvement efforts.
FAQ 4: What is the significance of the analysis stage in process improvement?
Answer: The analysis stage plays a vital role in process improvement as it helps in identifying root causes, bottlenecks, and areas where improvements can be made. Through data analysis and techniques such as root cause analysis, process mapping, and flowcharting, areas for optimization and enhancement are identified. It enables targeted improvements rather than making arbitrary changes.
FAQ 5: How does the improvement stage impact the overall process?
Answer: The improvement stage is where the identified improvements and solutions are implemented. It aims to optimize the process, eliminate or minimize inefficiencies, and enhance overall performance. By incorporating changes based on data and analysis, the improvement stage ensures that the process becomes more effective, efficient, and aligned with desired outcomes.
FAQ 6: Why is control important in process improvement?
Answer: Control is important in process improvement to ensure that the implemented improvements are sustained over time. It involves monitoring the performance of the process, collecting and analyzing data, and taking corrective actions when necessary. Control ensures that the process remains stable, delivers consistent results, and enables continuous improvement by identifying new opportunities for enhancement.
















Leave a Reply