What are the Requirements of ISO 9001?

ISO 9001 is a globally recognized standard for quality management systems. Discover the essential requirements of ISO 9001 and how they can benefit your organization in the article answering the question: What are the Requirements of ISO 9001?
Overview of ISO 9001
ISO 9001 is an internationally recognized standard for quality management systems (QMS). It provides a framework that organizations can follow to ensure that their products and services consistently meet customer requirements and enhance customer satisfaction. ISO 9001 sets out the criteria for a QMS and focuses on key principles such as customer focus, leadership commitment, involvement of people, process approach, continual improvement, evidence-based decision making, and relationship management.
The standard is applicable to any organization, regardless of its size or the industry it operates in. By implementing ISO 9001 quality management standards, organizations can establish an effective quality management system that enables them to monitor and improve their processes, identify and address potential risks, and drive continual improvement across the entire organization.
The requirements of ISO 9001 encompass various areas such as management commitment, customer satisfaction, process management, documentation and record keeping, internal audits, corrective actions, and management reviews. By meeting the requirements of ISO 9001, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to quality management system standards and ensure that their products and services consistently meet the needs and expectations of customers.
Purpose of ISO 9001
ISO 9001 is an international standard that provides quality management system requirements for organizations. Its purpose is to ensure that organizations meet customer needs, enhance customer satisfaction, and continually improve their processes and products or services.
ISO 9001 focuses on creating and implementing policies, processes, and procedures that meet customer and regulatory requirements. This includes establishing a quality policy that outlines the organization’s commitment to meeting customer needs and enhancing customer satisfaction. It also involves adopting a process approach, which means identifying and managing the various interrelated activities and resources required to deliver quality products or services.
The ISO standard emphasizes the importance of continual improvement by setting quality objectives, conducting internal audits, and regularly reviewing the performance of the quality management system. It also highlights the need for effective leadership and the involvement of the entire organization in the pursuit of quality.
ISO 9001 requires organizations to engage in performance evaluations, manage risks and opportunities, and establish relationships with external providers. It also emphasizes the importance of measuring customer satisfaction and seeking feedback to improve customer experiences.
By adhering to the requirements of ISO 9001, organizations can establish an effective quality management system that ensures their products and services consistently meet customer requirements, while also driving continual improvement and compliance with regulatory standards.
Quality Management Principles
Quality Management Principles serve as the foundation for ISO 9001. These principles guide organizations in establishing and implementing an effective quality management system. The seven principles of quality management are customer focus, leadership, engagement of people, process approach, improvement, evidence-based decision making, and relationship management.
Customer focus entails understanding and meeting customer requirements and continually enhancing customer satisfaction. Leadership involves establishing a clear vision, providing direction, and promoting a culture of quality. Engagement of people recognizes the importance of empowering and involving employees at all levels.
The process approach emphasizes the need to understand and manage interrelated processes to achieve desired outcomes. Improvement encourages the organization to continuously improve its processes, products, and services. Evidence-based decision making emphasizes the importance of using data and information to make informed decisions. Relationship management focuses on building and maintaining mutually beneficial relationships with external providers. By following these principles, organizations can establish a strong foundation for quality management and achieve ISO 9001 certification.
Customer Focus
Customer focus is an essential aspect of ISO 9001, as it plays a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness of a quality management system. By placing the customer and their requirements for products at the center of all activities, organizations can better meet their needs and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
In order to demonstrate customer focus, organizations must first understand the specific requirements of their customers. This includes comprehending their expectations, needs, and any service provision. By gathering this information, organizations can tailor their processes and products/services accordingly.
Open communication is vital for establishing and maintaining customer focus. Organizations must actively engage with their customers to gather feedback, address concerns, and resolve any issues. Regular customer reviews allow organizations to evaluate the effectiveness of their quality management system and make necessary improvements.
Monitoring and measuring quality levels is instrumental in maintaining customer focus. By using performance metrics and utilizing tools like customer satisfaction surveys, organizations can identify areas of improvement and take corrective actions accordingly.
Lastly, evidence of conformity is crucial in demonstrating customer focus. Organizations must provide evidence that their products or services meet customer requirements. This includes maintaining records of product/service characteristics, as well as ensuring compliance throughout the entire supply chain.
In conclusion, customer focus is critical in ISO 9001 as it ensures organizations align their processes and products with customer requirements. By actively engaging with customers, monitoring quality levels, and providing evidence of conformity, organizations can enhance customer satisfaction and continuously improve their quality management system.
Leadership
The leadership team plays a crucial role in implementing and maintaining ISO 9001 standards within an organization. As outlined in the ISO 9001 requirements, senior management is responsible for developing and establishing a robust quality management system (QMS). This involves defining quality policies and objectives that align with the organization’s strategic goals and customer requirements.
One of the primary responsibilities of leadership is effectively communicating the quality policies and objectives to all employees. This ensures that every individual in the organization is aware of the organization’s commitment to quality and understands their role in achieving it.
Leadership is also responsible for conducting periodic evaluations of the QMS to assess its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. This includes monitoring key performance metrics, conducting internal audits, and reviewing customer feedback. By regularly reviewing and analyzing these factors, leadership can make informed decisions to drive continual improvement.
Additionally, leadership must ensure that adequate resources are allocated to implement and maintain the QMS. This includes providing the necessary training and support to employees, as well as maintaining infrastructure and equipment in accordance with ISO 9001 standards.
In summary, leadership is pivotal in developing, implementing, and maintaining a successful QMS. Their responsibilities include developing quality policies and objectives, communicating them to employees, conducting periodic evaluations, and ensuring the availability of resources for effective quality management.
Engagement of People
Engagement of people is more than a human resources concern. It plays a crucial role in the successful implementation of ISO 9001. When all members of an organization are actively involved in the implementation process, it creates a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the quality management system (QMS).
By engaging people at all levels, organizations can harness the collective knowledge and expertise of their workforce. This collaboration leads to the identification of potential risks, opportunities for improvement, and innovative solutions. The involvement of employees also helps to build a culture of continuous improvement, where everyone is committed to delivering quality products and services.
When employees are engaged in ISO 9001 implementation, they are more likely to embrace the QMS and understand its purpose. This awareness fosters a greater understanding of customer requirements and expectations, resulting in enhanced customer satisfaction. Engaged employees are more motivated, leading to increased productivity, reduced errors, and higher quality products or services.
Furthermore, engagement of people is not limited to internal stakeholders. ISO 9001 also emphasizes the importance of relationship management with external providers. By establishing effective relationships with suppliers and other external partners, organizations can ensure the continuity of the supply chain. This includes managing supplier performance, monitoring the quality of inputs, and collaborating on process improvements.
In conclusion, engagement of people in ISO 9001 implementation brings numerous benefits to organizations. It fosters a culture of quality, drives continuous improvement, enhances customer satisfaction, and ensures the continuity of the supply chain. By involving all members of the organization, from leadership to frontline employees, organizations can achieve the full potential of their quality management system and thrive in today’s competitive business environment.
Process Approach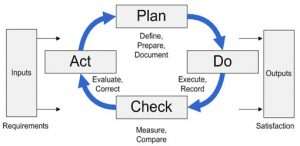
The process approach or PDCA (Plan Do Check Act) is a key concept in ISO 9001 that emphasizes the importance of understanding and managing the interconnected processes within an organization. By considering the inputs, activities, and outputs of each internal process, organizations can ensure that they are working together effectively to deliver high-quality products and services.
By adopting the process approach for your business processes, organizations can identify and address potential bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and risks that may impact the quality of their products or services. It allows them to streamline their operations, optimize resources, and improve overall performance. The process approach also enables organizations to have a better understanding of their customer requirements and align their processes accordingly.
During the certification process, there are six controls and checkpoints that need to be evaluated and monitored to ensure compliance with ISO 9001 requirements. These controls include management commitment, employee engagement, documentation control, corrective action, internal audits, and performance evaluation. By consistently assessing and reviewing these controls, organizations can identify areas for improvement and take necessary actions to maintain a robust quality management system.
Implementing process improvements is crucial for the continued success of an organization. It allows for the identification and elimination of non-value-added activities, resulting in improved workflows, increased efficiency, and reduced waste. Continuous process improvements also enhance customer satisfaction by ensuring that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations. By regularly evaluating and optimizing their processes, organizations can consistently deliver high-quality products and services and stay ahead in a competitive market.
Improvement
Improvement is a fundamental concept in ISO 9001 that plays a vital role in enhancing product quality, customer satisfaction, and meeting consumer demands. ISO 9001 emphasizes continual improvement as a critical component of a quality management system, encouraging organizations to constantly evaluate their processes and seek ways to enhance them.
By actively pursuing improvement opportunities, organizations can identify and address nonconformities or deviations from desired outcomes. This proactive approach allows businesses to rectify issues promptly, preventing their recurrence and minimizing the impact on product quality.
Furthermore, continual improvement enables organizations to stay responsive to evolving customer needs and expectations. By continuously evaluating customer feedback and market trends, companies can adapt their processes to better meet consumer demands and increase customer satisfaction.
ISO 9001 provides a structured framework for identifying improvement opportunities and implementing corrective actions. This systematic approach ensures that organizations uphold their commitment to quality and consistently strive for excellence in all aspects of their operations.
In conclusion, improvement is integral to ISO 9001 as it serves as a catalyst for enhancing product quality, enhancing customer satisfaction, and ensuring continued success in today’s competitive marketplace. By embracing continual improvement, organizations can cultivate a culture of excellence, drive innovation, and effectively meet the evolving demands of their customers.
Evidence-Based Decision Making
ISO 9001 emphasizes the importance of evidence-based decision making, recognizing that accurate and reliable data is indispensable for making informed business decisions. This approach ensures that organizations have a solid foundation for continuous improvement.
Competent staff members play a crucial role in this process by analyzing and evaluating all available data using appropriate tools and methods. By doing so, they can identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. This data-driven approach allows organizations to make decisions based on objective evidence rather than relying on assumptions or intuition.
Establishing a basis for increasing the effectiveness of the quality management system and achieving improved results is a fundamental requirement of ISO 9001. By using reliable and accurate data, organizations can identify areas where performance is below expectations and take appropriate corrective actions to address them. This systematic approach allows businesses to continuously improve their processes, products, and services, leading to increased customer satisfaction and overall organizational success.
In conclusion, evidence-based decision making is a key aspect of ISO 9001, ensuring that organizations base their actions on objective and reliable data. By utilizing competent staff members to analyze this data, organizations can identify improvement opportunities and continuously enhance their quality management system.
Relationship Management
Relationship management plays a crucial role in ensuring the continuity and success of the supply chain in the context of ISO 9001. ISO 9001 emphasizes the importance of maintaining strong and effective relationships with relevant partners, including but not limited to business associates, vendors, investors, and resellers.
Establishing and nurturing these relationships contribute to the smooth and efficient flow of goods, services, and information throughout the supply chain. Collaborating with these partners allows organizations to better understand and address their specific needs, preferences, and requirements. This understanding leads to better communication, coordination, and alignment, ultimately fostering a relationship built on trust and mutual benefit.
By actively managing relationships with relevant partners, organizations can proactively address potential risks and challenges, thereby ensuring the continuity of the supply chain. This includes factors such as supplier qualifications, monitoring supplier performance, ensuring the availability of necessary resources, and managing any changes or disruptions that may occur.
Successful companies place a strong emphasis on relationship management and recognize its impact on the overall success of their business. By fostering strong and collaborative relationships with relevant partners, organizations can enhance their competitive advantage, increase their ability to adapt to change, and ultimately deliver high-quality products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
Quality Management System Requirements
Quality management system requirements refer to the set of criteria and standards that organizations must meet in order to achieve ISO 9001 certification. These requirements are designed to ensure that organizations have strong processes, procedures, and quality management practices in place to consistently deliver products and services that meet customer requirements and expectations.
The ISO standard outlines a number of key areas that organizations must address, including leadership and commitment, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and improvement. In order to meet these requirements, organizations must establish a clear quality policy, set measurable quality objectives, implement a process-oriented approach, conduct regular internal audits, and continually strive for improvement. By adhering to these requirements, organizations can establish an effective quality management system that not only enhances customer satisfaction but also drives overall business performance and success.
Quality Manual
The Quality Manual is a significant document that serves as a comprehensive guide to an organization’s quality management system in relation to ISO 9001. It outlines the policies, processes, and procedures that the organization follows to ensure the delivery of quality products or services.
In the Quality Manual, the organization’s quality policy is described, emphasizing the company’s commitment to meeting customer requirements and complying with relevant regulations and standards. It also states the scope of the quality management system, outlining the boundaries of the organization’s activities.
The Quality Manual includes documented procedures that detail the steps and methods for performing certain tasks or processes, ensuring consistency and effectiveness. These procedures may cover various aspects such as product development, internal audits, corrective actions, and supply chain management.
Other essential components of the Quality Manual are the documentation requirements, including the mandatory documents that need to be developed and maintained by the organization. This could include records such as equipment calibration records, provision change control records, and service requirements review records.
Overall, the Quality Manual provides a comprehensive overview of the organization’s quality management system, serving as a reference for employees and a communication tool for customers and stakeholders. By following the guidelines set out in the Quality Manual, organizations can establish and maintain an effective and efficient quality management system in accordance with ISO 9001 standards.
Documented Information Requirements
ISO 9001 requires organizations to maintain certain documented information as part of their quality management system. This includes mandatory documents, such as the quality policy, quality objectives, scope of the quality management system, and management review minutes. These documents provide a framework for ensuring that the organization’s quality management system is effective and aligned with its business objectives.
However, it is important to note that ISO 9001 allows for customization of the documented information based on the specific needs of the organization. This means that businesses have the flexibility to tailor these documents to their unique circumstances, processes, and requirements. This customization process enables organizations to develop a quality management system that aligns with their business goals, industry standards, and regulatory obligations.
Customization also ensures that the documented information is relevant, up-to-date, and accessible to the relevant personnel. It allows organizations to clearly communicate their quality objectives and policies to employees, customers, and stakeholders, thereby enhancing their understanding and commitment to quality.
In conclusion, ISO 9001 mandates certain documents as part of the quality management system, but also emphasizes the need for customization. By customizing the documented information, organizations can effectively implement and maintain a quality management system that is tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
Control of Documents
The control of documents is a crucial requirement in ISO 9001 to ensure the effective implementation of a quality management system. While ISO 9001 has become less prescriptive regarding the number of required documents, it is still essential to have key documents in place to support the QMS.
These documents include the quality policy, which outlines the organization’s commitment to quality; quality objectives, which define the goals to be achieved; and the scope statement, which outlines the boundaries of the QMS.
Procedures are another important document in the control of documents requirement. These procedures provide step-by-step instructions on how specific processes should be carried out within the organization. Work instructions, on the other hand, provide more detailed guidance on how to perform specific tasks or activities.
Forms are also necessary documents as they are used to capture and record information related to quality processes and activities. Process maps can also be included to provide a visual representation of how processes are linked and flow within the organization.
The control of documents requirement ensures that these documents are properly maintained, reviewed, and updated as necessary. It also ensures that the appropriate versions are available to the relevant personnel when needed.
In conclusion, while ISO 9001 allows for flexibility in the number and customization of required documents, it is still important to have key documents such as the quality policy, quality objectives, scope statement, procedures, work instructions, forms, and process maps to support the effective implementation of a quality management system.
Control of Records
One of the requirements in ISO 9001 is the control of records, which ensures that relevant records are properly identified, stored, and maintained throughout their retention period. This requirement applies to all records that demonstrate compliance with procedures, the quality policy, objectives, and work instructions.
Records play a crucial role in providing evidence of conformity to established processes and requirements. These documents serve as a tangible proof that the organization is following the prescribed procedures and guidelines. By maintaining accurate and up-to-date records, companies can monitor and assess the effectiveness of their quality management system.
The control of records also extends to the treatment of customer’s property. It is essential to handle customer-owned materials or assets with care, and maintain records of their storage, use, and any damage incurred during their possession. This helps in demonstrating the organization’s commitment to meeting customer requirements and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Proper storage and maintenance of records are necessary to ensure their availability and accessibility when needed. This includes storing records in appropriate conditions to prevent deterioration or damage. By implementing effective controls over records, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to quality management principles and meet regulatory requirements.
Requirements of ISO 9001
ISO 9001 emphasizes the importance of controlling records to provide evidence of compliance, ensure the careful treatment of customer’s property, and maintain the integrity and accessibility of records throughout their retention period. By adhering to these requirements, organizations can enhance their quality management systems and continuously improve their overall performance.

















Leave a Reply