Quality Management System in 10 Easy Steps
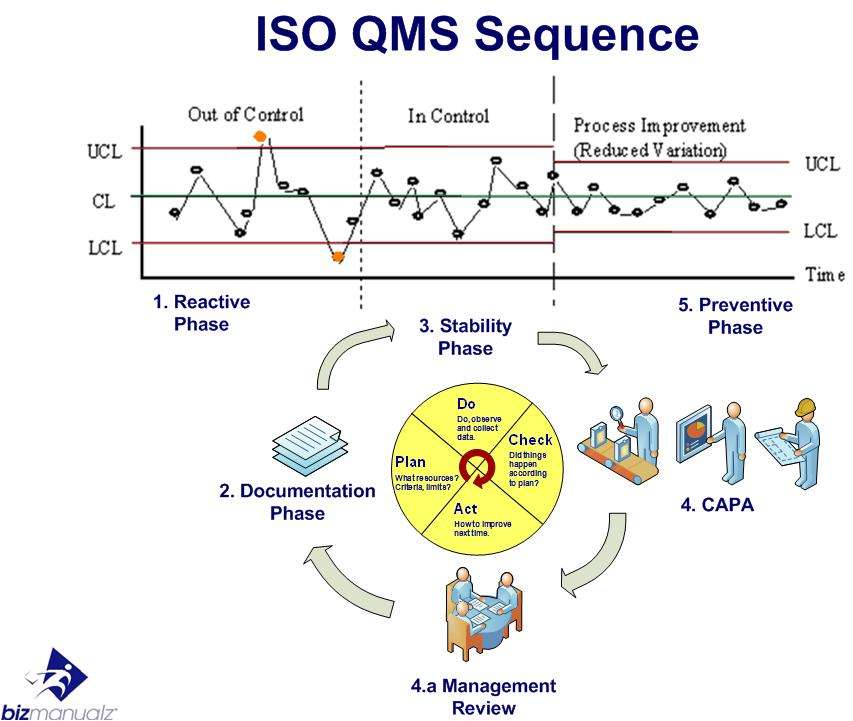
A Quality Management System (QMS) is a management system pure and simple. It is not quality’s management system; it is a management system that, if done right, produces quality products. A Quality Management Systems is built for ISO registration, to satisfy customer requirements, or to produce better products. Building a Quality Management System in 10 easy steps is not hard if you follow these steps.
How to Build a Quality Management System
A Quality Management System (QMS) is a management system that results in high-quality goods. To build a QMS, start by determining your processes, quality policy, quality objectives, your defects, processes, and training gaps, then measure, monitor, and improve.
 1. Define and Map Your Processes
1. Define and Map Your Processes
The process of creating process maps will force you to define your processes and the sequence and interaction of those processes (clause 4.4). Process maps are important for understanding who is responsible for what. They define your core business process and communicate the flow of your business.
When mapping your processes:
- Follow an order through the system.
- Identify support processes for IT, HR, and Accounting.
- Determine how quality interacts with each process either for inspection, review, or to roll-up metrics in support of Quality Objectives.
2. Define Your Quality Policy
Your Quality Policy states the mission (what your customer wants from you) of your organization as it relates to quality. It is your quality mission.
When building your quality management system and writing your quality policy, think about your commitment to customer focus:
- Quality – What do you need to do consistently to satisfy your customer?
- Customer Satisfaction – What are your customer’s requirements?
- Continuous Improvement – What do you need to do better to satisfy your customer more than now?
3. Define Your Quality Objectives
These are the objectives of the quality management system. They must be communicated and each employee must understand their impact on quality.
ISO requires that your quality objectives are:
- Derived from your quality policy
- Measureable
- Deployed through the organization
4. Define Your Defects for Each Process
Defects are nonconformances that occur either as a product defect or a process defect. Each time a defect occurs it needs to be counted, corrected, and determined whether corrective action is required. When defining your defects:
- Determine transaction volume
- Determine defects (product and process based)
- Define how defects are recorded
- Define how defects are charted and communicated
 5. Develop Your Documents and Records
5. Develop Your Documents and Records
ISO 9001:2015 requires some documented information (records). There are many more optional documents and records that can be used but they are not required. Start with the minimum ISO document set and add more as needed.
- Create required document information for your business model
- Create necessary Quality policies, procedures and forms, like found in our ISO 9001 2015 Procedures
- Create documented information (records) for each processes
6. Define Your Quality Process
Your quality processes include:
- Internal audit process

- Corrective and preventive action process
- Management review, communication, and commitment process
7. Determine Your Training Needs
Everyone needs to demonstrate competence in their job. Training is only the beginning and can occur on the job, from a class, or through other means. Either way:
- Internal auditor competence is critical
- Corrective Action training is highly recommended
- Failure Modes Effects Analysis (FMEA) training is strongly suggested for risk identification, prioritization, and action.
8. Use Your Quality Management System
Yes you have to use the quality strategies to improve the quality management system for it to be any good at producing quality products.
Using the QMS means:
- Collecting nonconformance data continuously
- Reviewing nonconformance data for corrective action, continuously
- Reviewing FMEAs for risk actions, frequently
- Performing internal audits and management reviews periodically
9. Measure and Monitor Your Performance
If you are using the quality management system, then you are collecting data. But what good is data you collect but do not understand?
You need to:
- Track your Quality Objectives performance
- Define new performance benchmarks
- Discover improvement opportunities in your data by identifying trends, patters, or correlations
10. TAKE ACTION That Improves Your Performance
If you have data and identified trends, then it is time to act. Action is what the QMS is all about, either corrective action or preventive action, but take action. We are not tracking data for the auditor, for ISO, or for the quality manager.
The whole goal is to deliver improvement and this happens by:
- Prioritizing your improvement opportunities
- Choosing opportunities that make a difference
- Reinforcing your commitment to quality to achieve better results
Build a Quality Management System
Whether you realize it or not, the management system you are using is a quality management system. So why not do it right and build a QMS to produce products with real quality? Bizmanualz is here to help you build a lean ISO quality system that delivers real value and rewards.















Leave a Reply