What is a Process and Its Elements?

To gain a comprehensive understanding of the subject, delve into the introduction of process elements. Define the process and explore the significance of comprehending its various elements. This exploration will shed light on the essential concept and emphasize the relevance of understanding this fundamental aspect. What is a process and its elements?
Definition of process
Processes are the motors that propel organizations towards their goals. They create structure, order, and efficiency for complex tasks and operations. A series of steps or actions need to be taken to reach a desired outcome, making sure results are consistent and of good quality.
First, objectives have to be identified. Then, resources are allocated, timelines are determined, and duties are given out during the planning stage. This prepares everything that is needed before the execution phase.
Execution is when the plan is put into action. Each step is done as per the previously defined guidelines. Communication between team members is key during this stage, to make sure tasks are finished on time.
Through the process, monitoring and control are fundamental. Progress is checked against the set objectives. Any risks are identified and stopped. And any changes from the plan are taken care of quickly. This helps keep everything clear and adaptable, so the process keeps going.
A great example is from manufacturing. A well-known car company was having a lot of delays because their machinery was malfunctioning. The management decided to introduce a preventive maintenance process. Regular inspections and repairs were planned, which greatly reduced downtime and increased productivity.
Importance of understanding process and its elements
Gaining insight into the process and its elements is very important. This comprehension allows individuals to recognize how a system or procedure works, making it possible for them to make informed decisions and improvements. Without this understanding, one may find it difficult to manage or improve processes, leading to poor results.
Why is understanding process and its elements essential? First, it helps troubleshoot issues quickly. By figuring out how different components interact within a process, individuals can identify bottlenecks more effectively. This lets them implement specific solutions that address root causes.
In addition, understanding the process and its elements aids in better coordination and collaboration within a team. When people have an understanding of each element’s role and contribution, they can work together to meet objectives. This increases productivity, reduces confusion, promotes creativity, and strengthens team unity.
Moreover, understanding process and its elements encourages continuous improvement efforts. With this knowledge, individuals can find opportunities for optimization or development. They can assess current practices against desired outcomes and make necessary adjustments. This iterative approach ensures that processes remain efficient and effective.
To make the most of understanding process and its elements, here are some useful tips:
- Conduct regular training sessions to teach employees about relevant processes assists in building their knowledge.
- Have open communication channels between team members helps them to share ideas for potential improvements.
- Use visual representations such as flowcharts or diagrams can help simplify complex processes. These visuals give a clear view of each element’s connections, making it easier to understand the whole structure.
- Have a culture of continuous learning encourages ongoing exploration and understanding of processes among employees. It allows individuals to gain a deeper understanding of their work environment, resulting in better insights and problem-solving abilities.
The Elements of a Process
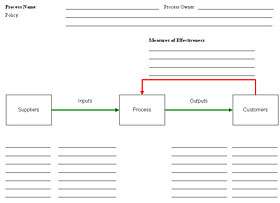
Process Template for Writing Procedures
To understand the elements of a process in “The Elements of a Process,” delve into the solution with “Process Inputs, Process Steps, Process Outputs.” Explore the individual components that contribute to the overall flow and outcomes of the process.
Process Inputs
Let’s dive deep into Process Inputs. Check out this table! It shows all the inputs needed for a process and their importance.
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
| Raw materials | Basic components used to create the final product |
| Tools and equipment | The necessary tools and machinery for the process |
| Information and data | Relevant knowledge or data required for decision-making |
| Personnel | Skilled individuals responsible for managing the process |
| Financial resources | Capital or funding necessary to facilitate the process |
| Time | Duration allocated for completing each step |
There’s more though. Quality control measures, regulatory compliance, and environmental considerations must also be taken into account. To optimize your process inputs, consider:
- Analyze possible bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
- Set up clear communication channels between team members.
- Monitor and evaluate inputs regularly.
These steps make problem-solving easier and use resources better. Monitoring helps you stay updated on changes, and you can adapt quickly.
Definition and explanation of process inputs
Process inputs refer to the necessary resources or materials for a process to start and finish. These vary, based on the process and its objectives. They are vital in deciding the result of a process and affect its proficiency and effectiveness.
Have a look at the table below to know some common examples of process inputs:
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
| Raw materials | Materials used for the production of goods or services |
| Information | Data or knowledge for decision-making and planning |
| Equipment | Tools or machinery to perform tasks |
| Human resources | Skilled individuals contributing their abilities |
Apart from these inputs, other factors like time, energy, and financial resources may be crucial for certain processes. Each input plays a critical role in making a process successful, thus emphasizing its importance in getting the desired outcome.
It is noteworthy that the quality and availability of process inputs can have a major effect on the performance and success of a process. Poor inputs can lead to inferior results, while high-quality inputs often create superior outcomes. That’s why it is critical for organizations to assess their input needs and get them from reliable sources.
As per a Harvard Business Review study, companies that prioritize investing in top-notch process inputs experience higher productivity, innovation, and customer satisfaction. This highlights the significance of grasping and valuing the role of process inputs in organizational success.
By understanding and optimizing the various elements that constitute process inputs, businesses can upgrade their operational capabilities and attain higher efficiency, leading to improved overall performance.
Examples of process inputs
Process inputs are the different elements needed for a process to be successful. Examples of these are:
– Raw Materials: These are the primary components used to make goods. For instance, steel and plastic are used to produce cars.
– Information: Data and knowledge are essential inputs in many processes. This can include customer details, market research, or any other appropriate facts to make decisions.
– Human Resources: Staff’s expertise and abilities are imperative in many processes. Whether it’s designing a new product or offering customer help, having the correct people with the right skills is essential.
– Technology: In the digital world, technology is often a key input in various processes. It can range from easy tools such as computers and software to more complex machinery and equipment.
– Finance: Money is another significant input in many processes. From getting funding for a project to managing cash flow, financial resources are often required for success.
These examples can be put in a table form:
| Inputs |
|---|
| Raw Materials |
| Information |
| Human Resources |
| Technology |
| Finance |
Process Steps
To make sure your process is successful, there are 6 steps to follow. Here’s the guide:
- State Objective: Clearly explain the purpose of the process & what you want to achieve. This sets the base for other actions.
- Analyze Needs: Work out the tasks, resources & restrictions needed to reach the goal. Assess what’s necessary for a smooth workflow.
- Make Plan: Draw out the order of activities, timelines & responsibilities for the process. Good planning leads to easy implementation.
- Execute Perfectly: Put your plan into practice by completing each task carefully & correctly. This’ll reduce mistakes & boost productivity.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly check if each step is being done how it should. It’ll let you make changes quickly & stop any blockages.
- Evaluate Results: Once finished, compare the outcome to the original objectives. Find any differences or areas for improvement.
Communication & collaboration are key too. A Harvard Business Review study found that companies that prioritize efficient processes have higher productivity & greater worker satisfaction.
Definition and explanation of process steps
A process is a combination of actions to get a desired result. These steps must be planned and done correctly to make sure they work. Let’s look deeper at the meaning of processes.
Here is a 6-step guide to help us understand:
- Define the goal: First, we need to know what needs to be done and why it is important.
- Divide it: Once we know the objective, we must break the process into sections that are easier to manage.
- Find connections: Some tasks depend on others. We need to find out which tasks are connected and in what order to do them.
- Assign roles: Each task should have one person in charge. Clarifying roles gives accountability and encourages teamwork.
- Track progress: We need to check the progress of the process frequently. This will let us make adjustments if needed and make sure we reach the goal.
- Review and improve: After the process is complete, look at how it worked. Find out what can be improved and adjust for future processes.
Each step in a process is necessary. Following these steps helps us explain our processes and reduce mistakes. A cool thing about processes is that they can be different in different contexts. Different businesses or organizations may have their own processes with specific steps that suit them. This shows how adaptable and changeable processes really are.
Processes have been around for a long time. From the factories in the industrial revolution to current project management methods, humans have been trying to make things simpler and more efficient. The development of processes shows our effort to do better.
Importance of following each step in a process
It’s key to follow each step of a process to get the desired result. This ensures accuracy, efficiency, and consistency. Skipping steps leads to errors, delays, and poor results. Here’s a 5-step guide to understanding the significance:
- Comprehend: First, understand the purpose and requirements. This creates a strong foundation and guarantees all steps align with objectives.
- Arrange: Next, order steps in a logical way. Each step should build on the last, leading to successful completion.
- Break Down: Break down the process into actionable tasks. This helps with organization and tracking progress.
- Consistent: Follow each step consistently. Even if some seem insignificant, they often contribute to effectiveness.
- Evaluate: Evaluate outcomes to identify areas for improvement. Get feedback from stakeholders and make necessary changes.
It’s not just going through motions. It needs attention to detail and diligent execution. Also, it fosters professionalism, increases productivity, reduces errors, builds trust, and optimizes resource use.
An example of this is the Apollo program. Adherence to each step ensured safe launches, landings, and return missions. Astronauts and ground control showed what happens when you don’t follow every step.
Process Outputs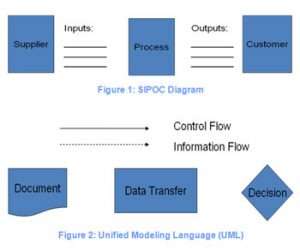
Let’s take a look at this table to understand the different types of process outputs.
| Type of Process Output | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Products | Tangible goods made in the process. |
| Reports | Documents summarizing findings, analyses, or progress. |
| Data Sets | Organized and structured info for further use. |
| Deliverables | Final products or services to clients. |
Process outputs are important in reflecting the effectiveness and efficiency of a process. By delivering these tangible and measurable results, organizations can show their value and create success.
It’s important to recognize that each output has unique details based on the process. Understanding these differences allows for better optimization and enhancement.
Pro Tip: Make sure your process outputs align with your goals and objectives. Evaluate their quality and relevance to get the most impact and drive improvement.
Definition and explanation of process outputs
Process outputs are the results and outcomes of a process. These can be tangible, like products, or intangible, like reports or analysis. They demonstrate the value created and are essential for reaching desired objectives.
Let’s look at the table below to understand process outputs better:
| Process Output | Definition |
|---|---|
| Product | Physical item resulting from a manufacturing or production |
| Report | Document presenting findings, analysis, or recommendations |
| Analysis | Examination and interpretation of data or information |
| Service | Performance of an activity to fulfill a specific need |
| Prototype | Early sample or model used for testing and validation |
Furthermore, each output has its own characteristics and serves a certain purpose within the context of the process. Knowing these details can help optimize the process and improve its effectiveness.
To make the best of process outputs, here are some tips:
- Define output requirements: Clarify what is acceptable for an output. This helps avoid misunderstandings and satisfies stakeholder expectations.
- Monitor output quality: Check quality of outputs to spot any issues or deviations from standards. This allows for prompt corrective actions and constant improvement.
- Streamline communication: Set up efficient channels for communication about process outputs. This encourages collaboration and ensures everyone has access to relevant updates.
If you follow these tips, you can improve efficiency, satisfy customers, and drive constant enhancement within your organization.
Examples of process outputs
Process outputs refer to products or services generated by a process. These can vary and have different goals based on the process. One way to show examples of process outputs is through a table. Here’s an example of a few:
| Process Output | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Reports | Provide information for decision-making |
| Products | Meet customer needs |
| Services | Meet customer needs |
| Data Analysis | Provide information to help with decisions |
It is important to remember that these are only some of the possible outputs. Depending on the process, there may be more. Analyzing process outputs helps companies understand their operations. It gives them ideas on how to improve the process for better outcomes.
Understanding the Process Flow
To understand the process flow, delve into the world of process flow diagrams and process mapping. Explore how these elements provide solutions and insights into the intricacies of a process. Uncover the visual representation of the flow and the systematic analysis that helps identify areas for improvement and optimization.
Process Flow Diagrams
Process Flow Diagrams are here to visualize a process. Symbols and lines represent tasks, decisions, inputs, outputs, and connections. Benefits? Clarity and analysis.
To make the best use of diagrams:
- Be accurate in depicting operations.
- Follow industry-standard conventions.
- Involve relevant stakeholders.
- Use software/tools specifically designed for process mapping.
- Review diagrams regularly.
Definition and purpose of process flow diagrams
Process Flow Diagrams (PFDs) are visual representations of the steps in a process. Symbols are used to make it easier to understand. Here’s a table explaining what they do and why they’re important:
| Definition | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Visual | Show process steps |
| Communication | Help with communication & understanding |
| Analysis | Find inefficiencies to improve |
| Documentation | Use as reference |
PFDs help train new staff and identify bottlenecks to streamline processes. Amazingly, they have been used since the 1920s when engineers drew them by hand. Today, technology helps us create them electronically with software.
Types of process flow diagrams
Process flow diagrams are a great way for visualizing and understanding complex processes. Symbols, arrows, and other elements help break it down into simpler steps. Here’s a table with different types and descriptions:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Linear Flow Diagram | Each step follows the previous in a sequential flow. |
| Functional Flow Diagram | Focuses on functions performed by each component. |
| Work Flow Diagram | Shows movement of tasks from one person/department to another. |
| Process Map | Gives a detailed overview of a process, with inputs & outputs. |
| Value Stream Map | Identifies value-added activities, removing non-value activities. |
To further improve process flow diagrams:
- Use color coding: Assign colors to different stages/actions.
- Include decision diamonds: Diamond-shaped symbols for decision points.
- Add data visualization: Show statistical/numerical data with graphs/charts.
These tips will increase clarity & effectiveness. Color coding adds visual appeal. Decision diamonds clearly present decision-making points. Data visualization makes it more engaging.
Process Mapping
Identify the Process: Process Mapping
Gather Information:
- Inputs: Data related to inputs, outputs, tasks, people, and timelines
- Outputs: Visual representation of the process map
- Tasks: Identifying and mapping the steps involved in the process
- People: Teams involved in the process
- Timelines: Timeframes for each step in the process
Create the Process Map:
Use software or draw a visual representation with shapes like rectangles and diamonds to create the process map.
Process Mapping gives insight into workflows. It helps teams streamline operations to be more efficient and effective, and it encourages collaboration.
Process Mapping has been used since ancient times. Egyptians and Romans used it to plan big projects like pyramids and aqueducts. Over centuries, it evolved into an important business practice for designing processes.
Definition and explanation of process mapping
Process mapping is a must-have when it comes to understanding and analyzing the steps in a process. It gives a visual representation of how tasks are interconnected and the flow of material or information.
- It uncovers the inefficiencies and bottlenecks, making it easier to make improvements.
- It boosts communication among team members by showing everyone their roles and duties.
- Seeing the dependencies between tasks facilitates better resource allocation and scheduling.
Analyzing a process requires finding inputs, outputs, and activities at each stage. This detailed research shows where time and resources can be saved, for enhanced productivity.
A good example of the power of process mapping is a manufacturing company that faced delays in their production line. By mapping out their processes, they found out certain steps that caused the problems. With this info, they could adjust those steps, leading to time savings and improved efficiency.
Techniques for creating process maps
- Figure Out the Process: Start by understanding what the process is, its inputs, outputs, and goals.
- Collect Details: Gather data and information about each step of the process. This could mean interviewing stakeholders or looking at existing documents.
- Pick Symbols and Shapes: Select symbols and shapes that represent different parts of the process, like activities, choices, or inputs/outputs. Keeping the symbols consistent is essential for easy reading.
- Make a Flowchart: Use software or a flowcharting tool to show the steps in the process in a visual way. Start with the first step and keep connecting the steps until you finish.
- Check and Improve: Get key stakeholders or experts to review and check the process map. Use their feedback to make it more accurate and easier to understand.
In addition, it’s important to go for simple over complex when making process maps. Keeping them short and easy-to-use will help everyone understand.
To make process maps that improve your workflows, use these methods. Don’t miss out on increasing efficiency start mapping your processes now!
Improving Processes
To improve processes, streamline and identify bottlenecks. In order to enhance efficiency, we will discuss two sub-sections: identifying process bottlenecks and streamlining process steps.
Identifying Process Bottlenecks
Process bottlenecks can get in the way of system efficiency. So, let’s explore various ways to detect these limitations and optimize processes.
Here’s a comprehensive table that presents different methods to identify process bottlenecks, their features, and benefits:
| Method | Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Time observation | Analyzes process duration | Finds areas for improvement in time management |
| Performance metrics | Measures system output | Highlights problem components or steps |
| Flowcharts | Visual representation | Helps pinpoint potential bottlenecks |
| Data analysis | Examines historical data | Uncovers patterns or trends that require attention |
Each approach provides unique insights to the system’s operation. By using time observation, you can spot tasks that take too long and find alternatives to streamline processes. Monitoring performance metrics can point out underperforming components or steps, allowing you to tackle them directly.
Flowcharts can be used to analyze processes. They give a clear overview of the workflow, which makes it easier to identify bottlenecks. Plus, data analysis lets you examine historical data and find trends or patterns that may require attention.
Pro Tip: When detecting process bottlenecks, make sure to get accurate data and conduct thorough analysis. Regularly monitoring and assessing performance metrics keeps processes efficient.
By utilizing these methods, you can detect process bottlenecks and take proactive measures to improve processes without compromising productivity. Continuous monitoring and reliable data analysis enable businesses to have a better understanding of their operations with precision and proficiency.
Definition and explanation of process bottlenecks
Process bottlenecks can cause delays and disruptions. They’re restrictions that slow down the workflow, and they’re usually found at production, supply chain, or customer service points.
Common causes are: inadequate resources, inefficient processes, lack of synchronization between departments, and poor communication. These can lead to increased costs, longer cycle times, lower customer satisfaction, and missed deadlines.
To cope, businesses need to make improvement efforts, depending on factors like impact and feasibility. Strategies like reallocating resources, streamlining processes, improving communication, and implementing technology solutions can help mitigate the issue. Monitoring and evaluation is also essential to recognize new bottlenecks.
Understanding and addressing process bottlenecks enables organizations to optimize their operations and enhance productivity. This has been researched extensively by Robert S. Kaplan and Michael E. Porter.
Techniques for identifying bottlenecks in a process
Identifying bottlenecks in your processes is vital for success. Pinpointing the areas that hinder progress enables businesses to be proactive and implement strategies to eliminate them. Here’s a four-step guide for effectively identifying these obstacles:
- Analyze Flow: Examine each step of the process. Identify potential points where delays happen.
- Gather Data: Collect time data for each step. Measure performance with quantitative metrics such as cycle or lead time.
- Identify Bottlenecks: Compare the data with industry standards. Deviations indicate potential bottlenecks.
- Dig Deeper: Investigate the root causes of the bottlenecks. Consider resource constraints, inadequate training, or outdated technology.
By addressing bottlenecks head-on, businesses can enhance productivity and streamline operations. Regularly review processes to identify emerging bottlenecks and take swift action. Continuous improvement is essential for maintaining efficiency and staying ahead of competitors.
Don’t let inefficiencies hold you back! Take action now and unlock your organization’s hidden potential by identifying and eliminating bottlenecks! Seize the chance before your competitors do and embrace this opportunity for growth. Act swiftly, analyze thoroughly, and unleash your full potential today!
Streamlining Process Steps
- Pinpoint Issues: Analyze data, interview people, get feedback from team members – find bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for improvement.
- Make it Simple & Standardize: After pinpointing, eliminate unnecessary steps and standardize the left ones – ensures consistency and less confusion.
- Automate Repetitive Tasks: Use tech to automate repetitive tasks – saves time and minimizes human mistakes. Try out workflow management tools, RPA, and AI.
- Monitor & Optimize: Streamlining processes is an ongoing effort – review the streamlined process regularly to identify any new inefficiencies or opportunities for further improvement.
Plus, effective communication between teams involved in the streamlined process is essential to avoid disruptions and maintain alignment throughout.
Innovative streamlining leads to improved operational efficiency and cost reduction.
Importance of eliminating unnecessary steps in a process
Henry Ford, in the early 1900s, revolutionized auto production. He got rid of superfluous steps and refined the process. This caused a great increase in efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Ford’s approach became a worldwide standard, showing the significance of cutting out unnecessary steps in any process.
Advantages of getting rid of needless steps:
- Streamlines Workflow: Taking out unimportant tasks simplifies the workflow and makes it easier to control.
- Saves Time: Unneeded steps lead to time wastage. Getting rid of them lets people focus on meaningful activities, raising productivity.
- Fewer Mistakes: Complicated processes raise the chances of errors. Taking out needless steps reduces the risk of errors.
In addition, eliminating unnecessary steps guarantees that standard procedures are consistently followed. This encourages better communication and team collaboration.
Methods for streamlining process steps
To enhance efficiency and productivity, there are many techniques to streamline process steps. Here’s a guide to help you get started:
- Pinpoint the bottlenecks: Identify which stages take the most time or cause delays.
- Simplify: Look for ways to simplify and remove unnecessary tasks or sub-steps.
- Use automation: Use tools and software to handle repetitive tasks, freeing up time for more complex activities.
- Create SOPs: Create detailed Standard Operating Procedures that clearly define each process step.
- Take advantage of technology: Explore tech solutions that can improve efficiency, such as project management software, collaboration tools, or analytics platforms.
- Monitor and optimize: Regularly review your streamlined processes, collect feedback, and make adjustments to further improve efficiency.
To make streamlining successful, you also need to foster a culture of continuous improvement. Encourage suggestions and recognize contributions. Streamlining is an ongoing effort that requires dedication and flexibility.
Here are some extra suggestions to consider:
- Form cross-functional teams: Gather individuals from different departments or areas of expertise to collaborate, communicate, and identify opportunities.
- Apply lean principles: Use Kanban boards or Lean Six Sigma to identify process waste and remove non-value-added activities.
- Invest in training: Train employees with the skills and knowledge needed to streamline processes.
- Foster innovation: Encourage employees to think outside the box and propose solutions for improving process efficiency.
- Review and update: Revisit and update processes to ensure they remain aligned with goals and objectives.
These suggestions can help businesses streamline process steps and create an agile, efficient, and productive work environment.
Process and Its Elements
To solidify your understanding of process and its elements, we will offer final thoughts on how you can apply this newfound knowledge in various industries or domains. Acquiring understanding of the procedure and its components is crucial.
This understanding enables people to identify the workings of a system or technique, enabling them to make adjustments and judgments based on knowledge. Without this knowledge, it could be challenging to control or enhance procedures, which could produce subpar outcomes.
















Leave a Reply