Understanding Target Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide

In “Understanding Target Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide,” you will explore the intricate world of target pricing and unravel its significance in the realm of business and accounting. This article aims to provide you with a holistic understanding of target pricing, delving into its definition, key concepts, and practical examples. By the end of this guide, you will have gained valuable insights into the importance of target pricing in achieving financial success and competitive advantage in the market. Understanding target pricing: a comprehensive guide.
Understanding Target Pricing
What is Target Pricing?
Target pricing is a strategic approach used by companies to determine the price at which a product or service should be offered in the market. It involves a thorough analysis of various factors such as costs, customer preferences, market competition, and desired profit margins.
The goal of target pricing is to set a price that not only covers costs and ensures profitability, but also aligns with the value perceived by customers and the prevailing market conditions.
Importance of Target Pricing
Target pricing plays a crucial role in the success of a business. By setting the right price, a company can maximize its profits, enhance competitiveness, and attract and retain customers.
Target pricing helps companies understand the value customers place on their products or services and enables them to align their pricing strategies accordingly. It also helps in optimizing costs and improving efficiency by assessing the financial feasibility of product development and production.
Factors Influencing Target Pricing
Several factors influence target pricing decisions. These include the company’s cost structure, market demand and elasticity, customer preferences, competitor pricing strategies, and desired profit margins.
It is essential for companies to consider these factors in order to determine a target price that is both profitable and marketable. Failure to account for these factors may result in pricing that is too high, leading to decreased demand, or pricing that is too low, resulting in reduced profitability.
Setting the Target Price
Basic Steps to Determine the Target Price
Setting the target price involves a series of steps that allow companies to calculate the optimal price point. The first step is to analyze the costs associated with the product or service. This involves identifying fixed and variable costs, as well as direct and indirect costs.
The next step is to perform market research to understand customer preferences and assess the pricing strategies of competitors. This information helps in identifying the optimal price range. Finally, companies should consider value analysis, which involves comparing the perceived value of their product with that of competitors and evaluating value-added features.
Considerations for Setting the Target Price
Companies must take into account various considerations when setting the target price. One important consideration is the cost structure. Companies should ensure that the target price covers all costs associated with the product or service, including production costs, distribution costs, and overhead costs.
Another consideration is the market demand and elasticity. It is important to assess how price changes may affect the demand for the product and adjust the target price accordingly. Additionally, companies should also consider the desired profit margin and evaluate the trade-offs between profitability and competitiveness.
Analyzing Costs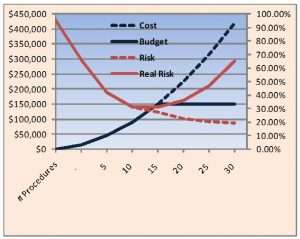
Cost Accounting Methods
Cost accounting methods help in determining the costs associated with the production of a product or service. These methods include job costing, process costing, and activity-based costing. Job costing is used when products are made to order, while process costing is used when products are produced in large quantities.
Activity-based costing allocates costs based on the activities that drive those costs. By using these methods, companies can accurately track and allocate costs, providing insights into the cost structure that are essential for target pricing decisions.
Standard Cost
Standard cost is the projected cost of creating a good or rendering a service under typical operating circumstances and using productive manufacturing techniques. It indicates the expense that a company anticipates accumulating based on the suppositions of effective resource utilization, ideal manufacturing procedures, and established criteria for supplies, labor, and overhead. In other words, it is a fixed cost that serves as a reference point for comparing real costs.
Fixed Costs and Variable Costs
In target pricing, it is important to distinguish between fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs are costs that do not change based on the level of production or sales volume. Examples include rent, salaries, and insurance.
Variable costs, on the other hand, change with the level of production or sales. These costs include raw materials, direct labor, and packaging. Understanding fixed and variable costs is crucial for determining the break-even point and setting the target price.
Direct Costs and Indirect Costs
Direct costs are costs that can be directly attributed to the production of a specific product or service. Examples include the cost of raw materials and direct labor. Indirect costs, also known as overhead costs, cannot be directly attributed to a specific product but are necessary for the overall operation of the business.
These costs include rent, utilities, and administrative expenses. Accurately allocating direct and indirect costs is important for determining the true cost of production and setting the target price.
Overhead Allocation
Overhead allocation refers to the process of assigning indirect costs to products or services. This is typically done using cost drivers, which are activities that consume resources and drive indirect costs.
By allocating overhead costs, companies can accurately determine the total cost of production and avoid under- or overpricing their products. Overhead allocation methods include traditional costing, which assigns costs based on volume-related measures, and activity-based costing, which allocates costs based on the activities that drive those costs.
Importance of Accuracy in Cost Analysis
Accurate cost analysis is essential for effective target pricing. Companies must have a clear understanding of their cost structure in order to set a target price that covers all costs and ensures profitability.
Inaccurate cost analysis can result in pricing that is either too high, leading to decreased demand, or too low, resulting in reduced profitability. Additionally, accurate cost analysis enables companies to identify areas of cost inefficiencies and take appropriate actions to improve their operations.
Market Research
Understanding Customer Preferences
Understanding customer preferences is crucial for target pricing. Companies need to gather data on what customers value in a product or service and how much they are willing to pay for it. This can be done through surveys, interviews, and focus groups.
By understanding customer preferences, companies can align their pricing strategies with the perceived value of their offerings, maximizing their chances of success in the market.
Identifying Competitors’ Pricing
Analyzing competitors’ pricing is an important aspect of target pricing. Companies need to gather data on the prices charged by their competitors for similar products or services.
This information helps in determining the competitive landscape and identifying opportunities for differentiation. By understanding competitors’ pricing strategies, companies can set their target price at a level that is competitive and attractive to customers.
Assessing Market Demand and Elasticity
Market demand and elasticity refer to the responsiveness of customers to changes in price. Understanding market demand helps companies assess the potential demand for their product or service at different price points.
Market elasticity, on the other hand, measures how changes in price affect the quantity demanded. By assessing market demand and elasticity, companies can determine the optimal price range that maximizes both profitability and market share.
Value Analysis
Determining Customer Perceived Value
Determining customer perceived value involves understanding how customers value a product or service relative to the price they are willing to pay. This can be done by analyzing customer feedback, conducting market research, and comparing the product to competitors.
By determining customer perceived value, companies can align their pricing strategies with what customers are willing to pay, increasing the likelihood of successful market penetration.
Comparing Perceived Value with Competitors
Comparing perceived value with competitors is an essential step in target pricing. By evaluating how customers perceive the value of their product or service in comparison to competitors, companies can identify areas of strength and weakness.
This information helps in setting a target price that is competitive and aligns with customer expectations. Companies that are able to offer superior value compared to their competitors can often command a premium price.
Evaluating Value-Added Features
Value-added features are additional features or enhancements that increase the perceived value of a product or service. By evaluating the impact of value-added features on customer perceived value, companies can determine if the costs associated with these features are justified.
This evaluation helps in setting a target price that not only covers costs but also reflects the value-added features. Additionally, value-added features can act as a competitive advantage, allowing companies to differentiate themselves from their competitors.
Competitor Analysis
Identifying Key Competitors
Identifying key competitors is an important step in target pricing. Companies need to analyze the competitive landscape and identify the direct competitors who offer similar products or services.
By understanding their competitors, companies can gain insights into their pricing strategies, market positioning, and value propositions. This information is essential for determining the target price and developing effective pricing strategies.
Analyzing Competitors’ Pricing Strategies
Analyzing competitors’ pricing strategies provides valuable insights into the market dynamics and helps in making informed pricing decisions. Companies should analyze the prices charged by competitors for similar products or services, as well as any discounts or promotions they offer.
This analysis helps in understanding the pricing norms in the industry and identifying opportunities for differentiation. By offering a price that is competitive and attractive to customers, companies can gain a competitive edge in the market.
Differentiating from Competitors
Differentiating from competitors is crucial for successful target pricing. Companies should identify and emphasize their unique selling points and value propositions. By offering something that competitors do not, companies can justify higher prices and differentiate themselves in the market.
Differentiation can be achieved through various means, such as superior product quality, exceptional customer service, or innovative features. By effectively differentiating from competitors, companies can enhance their pricing strategies and maximize their profitability.
Target Costing
Definition of Target Costing
Target costing is a proactive cost management approach that involves setting a target cost for a product or service and then designing and developing the product or service in a way that achieves that target cost.
Unlike traditional cost accounting approaches that focus on cost allocation, target costing focuses on cost reduction and value creation throughout the product lifecycle. By considering cost constraints from the early stages of product development, companies can align their design and production processes with target costs, resulting in more profitable pricing.
Steps in Target Costing
Target costing involves several steps to ensure effective cost management. The first step is to set the target cost, which is the maximum cost allowed for a product or service to achieve a desired profit margin. The next step is to conduct cost analysis, identifying the major cost drivers and areas for cost reduction.
Then, companies need to implement cost reduction activities by exploring various cost-saving options, such as process improvements or supply chain optimization. Finally, continuous monitoring and evaluation are necessary to ensure that the target cost is maintained and any deviations are addressed promptly.
Implementing Target Costing
Implementing target costing requires a cross-functional approach involving various departments within the organization. It starts with a clear understanding of customer requirements and aligning the target cost with market expectations.
Collaboration between design, engineering, production, and procurement teams is essential to identify cost reduction opportunities and implement design and process changes.
Additionally, effective communication and coordination with suppliers and vendors are crucial to optimize costs throughout the supply chain. Through effective implementation, target costing can help companies achieve profitability while maintaining competitive pricing.
Profit Margin Considerations
Determining Desired Profit Margin
Determining the desired profit margin is a critical step in target pricing. Companies need to define their profit objectives and align them with their overall business strategy.
Factors such as industry norms, market conditions, and investment requirements should be considered when determining the desired profit margin.
It is crucial to strike a balance between profitability and competitiveness, as setting profit margins too high may result in decreased demand, while setting them too low may compromise profitability.
Balancing Profit Margins and Competitiveness
Finding the right balance between profit margins and competitiveness is essential for long-term success. While higher profit margins may be desirable, excessively high prices can hinder a company’s market share and growth potential.
On the other hand, low profit margins may reduce profitability and limit resources for innovation and expansion. Companies must weigh the trade-offs between profit margins and competitiveness to ensure sustainable profitability while meeting customer demands and maintaining market share.
Flexibility in Pricing
Adjusting Pricing Strategies based on Market Conditions
Flexibility in pricing is important to adapt to changing market conditions. Companies should continuously monitor market dynamics, including changes in customer preferences, competitive pricing, and economic trends.
By analyzing these factors, companies can adjust their pricing strategies to remain competitive and capture market opportunities. Flexibility in pricing also enables companies to respond to fluctuations in input costs, supply chain disruptions, or changes in market demand, ensuring their pricing remains relevant and profitable.
Promotions and Discounts
Promotions and discounts are effective pricing strategies to attract and retain customers. Companies can offer limited-time discounts, bundle pricing, or loyalty programs to incentivize customers to make a purchase. Promotions can help companies increase sales volume, clear excess inventory, or introduce new products.
However, it is important to carefully plan and execute promotions to ensure profitability and avoid eroding the brand value. By strategically using promotions and discounts, companies can enhance their pricing strategies and drive customer engagement.
Long-term Price Management
Long-term price management involves a systematic approach to pricing decisions over an extended period. Companies should regularly evaluate their pricing strategies, taking into account changes in costs, market dynamics, and competitive landscape.
This long-term view helps in maintaining pricing consistency and profitability. It also allows companies to assess the impact of pricing decisions on customer retention, market share, and overall financial performance. Through effective long-term price management, companies can adapt to market conditions and maximize their profitability.
Monitoring and Evaluating Pricing
Tracking Variance from Target Price
Monitoring variance from the target price is crucial to ensure pricing decisions align with financial objectives. Companies should regularly compare the actual prices charged to the target price to identify any deviations. Significant variances may indicate the need for reassessment and adjustment of pricing strategies.
By tracking variance from the target price, companies can take timely corrective measures and ensure their pricing remains consistent with their cost structure and profitability goals.
Analyzing Pricing Strategies’ Effectiveness
Analyzing the effectiveness of pricing strategies is important to evaluate their impact on financial performance and market positioning. Companies should assess sales performance, profit margins, and market share to determine whether pricing strategies are yielding the desired results.
In addition, customer feedback and market research can provide insights into how customers perceive pricing and the value offered. By analyzing the effectiveness of pricing strategies, companies can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance their pricing strategies.
Continuous Improvement in Pricing
Continuous improvement in pricing involves an ongoing effort to refine pricing strategies and adapt to changing market conditions. Companies should regularly review their pricing processes, cost analysis methods, and market research to identify areas for improvement.
This includes evaluating pricing models, refining cost allocation methods, and exploring new pricing strategies. By embracing continuous improvement, companies can optimize their pricing strategies, enhance profitability, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Target Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide
In conclusion, understanding target pricing is crucial for companies aiming to establish profitable pricing strategies. By considering factors such as costs, customer preferences, market competition, and desired profit margins, companies can set a target price that aligns with market expectations and maximizes profitability. Analyzing costs accurately, conducting market research, evaluating customer perceived value, and differentiating from competitors are essential steps in determining the target price.
Implementing target costing, balancing profit margins with competitiveness, and adopting flexible pricing strategies enable companies to adapt to market conditions and enhance long-term profitability. Regular monitoring and evaluation of pricing, along with continuous improvement efforts, ensure that companies can make informed pricing decisions and stay competitive in the dynamic marketplace.
















Leave a Reply