When Revenues Are Reported: An Overview

Businesses, both small and large, face countless financial responsibilities, and revenue reporting is one of them. The Revenue Cycle is an essential component of any business operation as it forms the basis for calculating profits and other financial metrics. The timing of revenue recognition is critical for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders in determining a company’s financial health. Here we explain when revenues are reported: an overview for those new to accounting.
Understanding Revenue Reporting
Revenue reporting is a process of accounting for and disclosing a company’s earnings within a given period. This process involves identifying the sources of income and determining when the revenue is earned and recognized. The principal objective of revenue reporting is to ensure that financial statements accurately reflect a company’s financial performance.
Definition of Revenue Reporting
Revenue reporting is the process of accounting for and recognizing revenues earned by a business. It involves identifying the sources of revenue and determining the timing of revenue recognition. Revenue reporting is critical in determining a company’s profitability and financial health.
Revenue reporting is part of revenue management. The goal of revenue management is to maximize income by more effectively controlling the demand for goods and services. Your consumer base and their willingness to pay for your service or product can be optimized through this method.
Importance of Accurate Revenue Reporting
Accurate revenue reporting is vital for several reasons. It facilitates informed decision-making by providing stakeholders with a clear picture of a company’s financial status. Investors use revenue reports to determine a company’s current and future potential, while creditors use them to assess a company’s creditworthiness.
Moreover, regulatory bodies require companies to disclose their revenue and earnings reports to ensure compliance with financial reporting regulations. The accuracy of these reports is of utmost importance as errors or omissions can result in legal or financial consequences.
It is important to note that revenue reporting is not just a matter of adding up the money a company has earned. Rather, it involves a complex set of rules and principles that must be followed to ensure the accuracy and transparency of financial statements. For example, revenue recognition may be deferred for certain types of sales until the goods or services are delivered or until certain conditions are met.
Additionally, revenue reporting can vary depending on the industry and the type of business. For example, a company that sells products may recognize revenue differently than a company that provides services. Furthermore, companies operating in multiple countries may need to comply with different accounting standards and regulations.
Overall, accurate revenue reporting is essential for a company’s financial health and reputation. It provides stakeholders with the information they need to make informed decisions and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements. Therefore, companies must ensure that their revenue reporting processes are robust, transparent, and accurate.
Key Components of Revenue Reporting
Revenue reporting is a critical aspect of any business, and it comprises various components that help to determine the financial health of the organization. The different components of revenue reporting include sales revenue, service revenue, investment revenue, and other revenue sources.
Sales Revenue
Sales revenue is the most significant revenue source for many businesses, and it is generated by the sale of goods or services. This revenue source is recognized when the sale is made, and the transfer of ownership has occurred. Sales revenue is an essential component of revenue reporting as it helps businesses to determine the effectiveness of their sales strategies and the demand for their products or services.
For instance, a business that sells electronic gadgets can use sales revenue to determine which products are selling the most and which are not. This information can then be used to make informed decisions on which products to stock and which to discontinue.
Service Revenue
Service revenue is another critical component of revenue reporting, and it pertains to income generated by providing services to clients or customers. This can include consulting services, repair services, or maintenance services. Service revenue is typically recognized when the service has been provided.
For instance, a business that provides consulting services can use service revenue to determine which services are in high demand and which are not. This information can then be used to make informed decisions on which services to offer and which to discontinue.
Investment Revenue
Investment revenue comprises income from investments, such as stocks, bonds, and other securities. The revenue generated from these investments is recognized when dividends are received or interest is earned. Investment revenue is an essential component of revenue reporting as it helps businesses to determine the return on their investments and the effectiveness of their investment strategies.
For instance, a business that invests in stocks can use investment revenue to determine which stocks are performing well and which are not. This information can then be used to make informed decisions on which stocks to hold and which to sell.
Other Revenue Sources
Other revenue sources may include rental income, licensing fees, and other miscellaneous income. Revenue recognition for these sources varies depending on the nature of the revenue source. Other revenue sources are an essential component of revenue reporting as they help businesses to diversify their revenue streams and reduce their dependence on a single revenue source.
For instance, a business that generates rental income can use this revenue source to determine the effectiveness of their rental strategy and make informed decisions on whether to increase or decrease rental rates.
In conclusion, revenue reporting is a critical aspect of any business, and the key components of revenue reporting include sales revenue, service revenue, investment revenue, and other revenue sources. By understanding these components, businesses can make informed decisions on their sales, service, and investment strategies and diversify their revenue streams to ensure long-term financial stability.
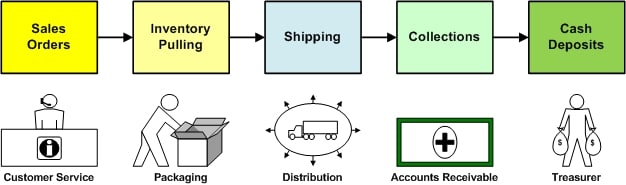
Revenue Process Map
Revenue Recognition Principles
Revenue recognition is a critical aspect of accounting for businesses. It is the process of recognizing revenue in a company’s financial statements, and it is essential for measuring a company’s financial performance accurately. Revenue recognition principles help businesses to determine when and how to recognize revenue in their financial statements.
Accrual Accounting vs. Cash Accounting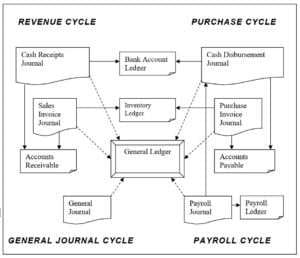
Accrual accounting and cash accounting are two methods of accounting for revenue recognition. Cash accounting recognizes revenue when cash is received, while accrual accounting recognizes revenue when it is earned, regardless of when the cash is received.
Accrual accounting is the preferred method of accounting for revenue recognition because it provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial performance over time. Accrual accounting allows businesses to recognize revenue when it is earned, even if the cash has not yet been received. This is important because it helps businesses to measure their financial performance more accurately.
For example, a company may provide services to a customer in one month but not receive payment until the following month. Under cash accounting, the revenue would not be recognized until the following month when the cash is received. However, under accrual accounting, the revenue would be recognized in the month when the services were provided, providing a more accurate picture of the company’s financial performance.
The Five-Step Revenue Recognition Process
The five-step revenue recognition process is a framework for recognizing revenue under the accrual accounting method. It includes identifying the contract with the customer, identifying the performance obligations, determining the transaction price, allocating the transaction price to the performance obligations, and recognizing revenue when the performance obligations have been satisfied.
- The first step in the revenue recognition process is to identify the contract with the customer. This involves determining the terms of the contract, including the goods or services to be provided, the price, and the payment terms.
- Once the contract has been identified, the next step is to identify the performance obligations. This involves determining the specific goods or services that will be provided under the contract.
- The third step in the revenue recognition process is to determine the transaction price. This involves determining the amount of revenue that will be recognized under the contract.
- The fourth step is to allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations. This involves determining how much of the transaction price should be allocated to each performance obligation.
- Finally, the fifth step is to recognize revenue when the performance obligations have been satisfied.
Common Revenue Recognition Challenges
Revenue recognition can be a complex and challenging process for businesses. Some common challenges include identifying the timing of revenue recognition, determining the transaction price, and allocating the transaction price to the performance obligations. Companies must be diligent in their revenue reporting to ensure that they comply with financial reporting regulations and avoid legal or financial consequences.
One common challenge in revenue recognition is identifying the timing of revenue recognition. This can be especially challenging for companies that provide services over an extended period of time. Companies must determine when revenue should be recognized based on the specific terms of the contract and the performance obligations.
Another common challenge in revenue recognition is determining the transaction price. This can be challenging when contracts include variable pricing or discounts. Companies must carefully consider the terms of the contract to determine the appropriate transaction price.
Allocating the transaction price to the performance obligations can also be a challenge. This involves determining how much of the transaction price should be allocated to each performance obligation. Companies must carefully consider the specific goods or services provided under the contract to determine the appropriate allocation.
In conclusion, revenue recognition is an essential aspect of accounting for businesses. Accrual accounting is the preferred method of accounting for revenue recognition because it provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial performance over time. The five-step revenue recognition process is a helpful framework for recognizing revenue under the accrual accounting method. However, revenue recognition can be a complex and challenging process, and companies must be diligent in their revenue reporting to ensure compliance with financial reporting regulations and avoid legal or financial consequences.
Reporting Revenues in Financial Statements
Revenues are the lifeblood of any business, and it’s crucial to report them accurately on financial statements. Financial statements provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial health and performance. In this article, we’ll explore how revenues are reported on the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
Income Statement
The income statement is also known as the profit and loss statement. It details a company’s revenue, expenses, gains, and losses for a given period. Revenue is the total amount of money a company earns from its operations, while expenses are the costs incurred to generate that revenue. Gains and losses refer to any non-operating income or expenses, such as the sale of assets or investments.
Net income is the bottom line of the income statement and is calculated as revenue minus expenses. It’s a primary indicator of a company’s profitability. Investors and analysts closely monitor a company’s net income, as it reflects the company’s ability to generate profits from its operations.
It’s important to note that revenue recognition principles dictate when and how revenue is recognized on the income statement. Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require companies to recognize revenue when it’s earned, regardless of when cash is received.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet presents a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a given point in time. It’s divided into two sections: assets and liabilities. Assets are the resources a company owns, while liabilities are the obligations it owes to others.
Revenue is reported under assets as a component of retained earnings or equity. Retained earnings represent the portion of a company’s profits that are not distributed as dividends but are instead reinvested in the business. Equity is the residual interest in the assets of a company after deducting liabilities. It represents the owners’ stake in the company.
Revenue is a crucial component of a company’s equity and retained earnings. As revenue increases, so does the value of a company’s equity and retained earnings. This, in turn, can lead to higher stock prices and increased investor confidence.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement details a company’s cash cycle of inflows and outflows for a given period. It provides crucial information regarding the timing of cash receipts and payments. As revenue is recognized independently of cash, the cash flow statement is essential in understanding a company’s liquidity and cash position.
Operating cash flow is the cash generated or used by a company’s operations. It’s calculated as net income plus non-cash expenses minus non-cash revenues. Investing cash flow is the cash used or generated by a company’s investments in assets such as property, plant, and equipment. Financing cash flow is the cash used or generated by a company’s financing activities, such as issuing or repurchasing stock or paying dividends.
The cash flow statement is a critical tool for investors and analysts in assessing a company’s financial health. Positive cash flow from operations indicates that a company’s core business is generating cash, while negative cash flow from operations may indicate underlying problems with the business.
In conclusion, reporting revenues accurately on financial statements is crucial for investors, analysts, and other stakeholders in assessing a company’s financial health and performance. The income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s revenues and how they’re generated and used. By understanding these statements, investors can make informed decisions about investing in a company.
Revenue Reporting
Revenue reporting is a fundamental aspect of any business’s financial operations. Accurate reporting enables stakeholders to make informed decisions, and regulatory bodies to ensure compliance. Recognizing revenue can be a complex process, and companies must be vigilant in identifying revenue sources, recognizing revenue, and reporting them accurately in their financial statements.















Leave a Reply